Discovery of Benzylpiperazine Derivatives as CNS-Penetrant and Selective Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitors
- PMID: 35859864
- PMCID: PMC9290043
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00081
Discovery of Benzylpiperazine Derivatives as CNS-Penetrant and Selective Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitors
Abstract
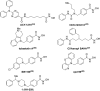
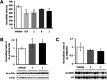
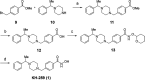
Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) in the brain is a highly attractive therapeutic target for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. The low blood-brain barrier permeability of most known HDAC6 inhibitors, however, prevents their application as central nervous system (CNS) drugs. To overcome this problem, we designed and synthesized benzylpiperazine derivatives using a hybrid strategy of combining HDAC6 inhibitors and brain-penetrant histamine H1 receptor antagonists. Introducing the benzylpiperazine units to the cap region of hydroxamate-type HDAC6 inhibitors led us to identify isozyme-selective and CNS-penetrant HDAC6 inhibitor KH-259 (1) with the appropriate pharmacokinetic and safety properties. Intraperitoneal administration of KH-259 (10 mg/kg) had antidepressant activity and increased acetylated α-tubulin in the brain without promoting acetylated histone H3K9. These findings indicate that our hybrid strategy of combining HDAC6 inhibitors and histamine H1 receptor antagonists is an effective methodology for designing CNS-penetrant HDAC6 inhibitors.
© 2022 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

