Asymmetric Cell Division and Tumor Heterogeneity
- PMID: 35859890
- PMCID: PMC9289117
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.938685
Asymmetric Cell Division and Tumor Heterogeneity
Abstract
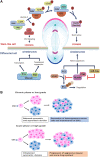
Asymmetric cell division (ACD) gives rise to two daughter cells with different fates after mitosis and is a fundamental process for generating cell diversity and for the maintenance of the stem cell population. The cancer stem cell (CSC) theory suggests that CSCs with dysregulated self-renewal and asymmetric cell division serve as a source of intra-tumoral heterogeneity. This heterogeneity complicates the diagnosis and treatment of cancer patients, because CSCs can give rise to aggressive clones that are metastatic and insensitive to multiple drugs, or to dormant tumor cells that are difficult to detect. Here, we review the regulatory mechanisms and biological significance of asymmetric division in tumor cells, with a focus on ACD-induced tumor heterogeneity in early tumorigenesis and cancer progression. We will also discuss how dissecting the relationship between ACD and cancer may help us find new approaches for combatting this heterogeneity.
Keywords: asymmetric cell division; drug resisitance; symmetric cell division; tumor heterogeneity; tumorgenesis.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Zhang, Zhang, Yang, Chen and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Asymmetric division of stem cells and its cancer relevance.Cell Regen. 2024 Feb 27;13(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13619-024-00188-9. Cell Regen. 2024. PMID: 38411768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Effectiveness of Anticancer Agents Targeting Different Signaling Molecules Involved in Asymmetric Division of Cancer Stem Cell.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023 Jul;19(5):1283-1306. doi: 10.1007/s12015-023-10523-3. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023. PMID: 36952080 Review.
-
Cell division symmetry control and cancer stem cells.AIMS Mol Sci. 2020;7(2):82-98. doi: 10.3934/molsci.2020006. Epub 2020 May 6. AIMS Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32953979 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of asymmetric cell division to phenotypic heterogeneity in cancer.J Cell Sci. 2024 Mar 1;137(5):jcs261400. doi: 10.1242/jcs.261400. Epub 2024 Feb 9. J Cell Sci. 2024. PMID: 38334041 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms controlling asymmetric and symmetric self-renewal of cancer stem cells.J Anal Sci Technol. 2015;6(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s40543-015-0071-4. Epub 2015 Oct 15. J Anal Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 26495157 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia-induced cancer cell reprogramming: a review on how cancer stem cells arise.Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 8;13:1227884. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1227884. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37614497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Density Gradient Centrifugation Is an Effective Tool to Isolate Cancer Stem-like Cells from Hypoxic and Normoxia Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 17;25(16):8958. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168958. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201646 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric cell division of ALDH1-positive cancer stem cells generates glycolytic metabolically diverse cell populations.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 22;15(1):13932. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97985-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40263471 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the interaction between redox signaling and senescence to restrain tumor drug resistance.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jul 9;13:1639772. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1639772. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40703657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asymmetric division of stem cells and its cancer relevance.Cell Regen. 2024 Feb 27;13(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13619-024-00188-9. Cell Regen. 2024. PMID: 38411768 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Armah H. B. (2010). Malignant Astrocytomas Originate from Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells in a Somatic Tumor Suppressor Mouse Model. Yearb. Pathology Laboratory Med. 2010, 171–172. 10.1016/s1077-9108(09)79438-1 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

