The Epigenetic Role of MiRNAs in Endocrine Crosstalk Between the Cardiovascular System and Adipose Tissue: A Bidirectional View
- PMID: 35859891
- PMCID: PMC9289671
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.910884
The Epigenetic Role of MiRNAs in Endocrine Crosstalk Between the Cardiovascular System and Adipose Tissue: A Bidirectional View
Abstract
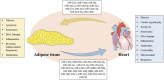
Overweight and obesity (OBT) is a serious health condition worldwide, and one of the major risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD), the main reason for morbidity and mortality worldwide. OBT is the proportional increase of Adipose Tissue (AT) compared with other tissue and fluids, associated with pathological changes in metabolism, hemodynamic overload, cytokine secretion, systemic inflammatory profile, and cardiac metabolism. In turn, AT is heterogeneous in location, and displays secretory capacity, lipolytic activation, insulin sensitivity, and metabolic status, performing anatomic, metabolic, and endocrine functions. Evidence has emerged on the bidirectional crosstalk exerted by miRNAs as regulators between the heart and AT on metabolism and health conditions. Here, we discuss the bidirectional endocrine role of miRNAs between heart and AT, rescuing extracellular vesicles' (EVs) role in cell-to-cell communication, and the most recent results that show the potential of common therapeutic targets through the elucidation of parallel and ⁄or common epigenetic mechanisms.
Keywords: adipose tissue; cardiovascular disease; crosstalk; heart; metabolism; microRNA; obesity.
Copyright © 2022 Soci, Cavalcante, Improta-Caria and Roever.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cross Talk between Adipose Tissue and Placenta in Obese and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Pregnancies via Exosomes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017 Sep 27;8:239. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00239. eCollection 2017. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017. PMID: 29021781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipocyte-Endothelium Crosstalk in Obesity.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Aug 12;12:681290. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.681290. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34456860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does microRNA Perturbation Control the Mechanisms Linking Obesity and Diabetes? Implications for Cardiovascular Risk.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 25;22(1):143. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010143. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33375647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intercellular and interorgan crosstalk through adipocyte extracellular vesicles.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2022 Feb;23(1):61-69. doi: 10.1007/s11154-020-09625-x. Epub 2021 Jan 14. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2022. PMID: 33447986 Review.
-
Fat-to-heart crosstalk in health and disease.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 24;14:990155. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.990155. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37035745 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Train and Reprogram Your Brain: Effects of Physical Exercise at Different Stages of Life on Brain Functions Saved in Epigenetic Modifications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 9;25(22):12043. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212043. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Epicardial Adipose Tissue-Derived MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Cardiovascular Disease: A Narrative Review.Biology (Basel). 2023 Mar 25;12(4):498. doi: 10.3390/biology12040498. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37106699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Bibliometric and Visual Analysis of EGR1 in Cardiovascular Disease.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Aug 29. doi: 10.1007/s12033-025-01493-7. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40880050 Review.
-
Early growth response-1: Key mediators of cell death and novel targets for cardiovascular disease therapy.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Mar 28;10:1162662. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1162662. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37057102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating miR-10b-5p, miR-193a-3p, and miR-1-3p Are Deregulated in Patients with Heart Failure and Correlate with Hormonal Deficiencies.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 29;26(11):5225. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115225. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avogaro A. (2006). Insulin Resistance: Trigger or Concomitant Factor in the Metabolic Syndrome. Panminerva Med. 48, 3–12. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

