Terminal digit preference and the accuracy of breast cancer diameter reporting based on Benford's law
- PMID: 35860050
- PMCID: PMC9289319
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103993
Terminal digit preference and the accuracy of breast cancer diameter reporting based on Benford's law
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is the most frequent cancer in women all over the world, and it is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths in women. A pathologist's partiality for the last digit of a patient's name can lead to errors in the measurement of malignancies. This means that, rather than recording the exact measurement of a tumor, a pathologist might round it off to his preferred terminal digit.
Methods: It is a retrospective cross-sectional study in which data on primary tumor resection for 1000 breast cancer patients was obtained from KRL Hospital's patient directory from November 2016 to December 2020. The tumors were measured in cm to one decimal point along their longest dimension. Ki-67 markers were used to categorize the tumors into nine categories. Terminal digit preference was evaluated using Benford's law.
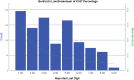
Results: The recording of the Ki-67 index revealed evidence of pentameric preference. The numbers three, five, and six appeared more frequently in the histogram of the Ki-67 index distribution measured in percentage. The frequency of nine dropped dramatically. However, the influence of tumor size terminal digits on Ki-67 staining scores (low proliferative vs high proliferative) assessed using the Mann-Whitney U Test demonstrated that tumor size terminal digits had no significant effect on Ki-67 staining scores (p = 0.114).
Conclusion: The Ki-67 index shows evidence of pentameric preference for digits three, five, and six. The frequency of nine has dropped dramatically. The influence of tumor size on terminal digits on staining scores (low proliferative vs. high proliferative) was assessed using the Mann-Whitney U Test.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None to disclose.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources