Network Pharmacology-Based Strategy to Reveal the Mechanism of Cassiae Semen against Cataracts
- PMID: 35860180
- PMCID: PMC9293494
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5654120
Network Pharmacology-Based Strategy to Reveal the Mechanism of Cassiae Semen against Cataracts
Abstract
Cassiae semen (CS) is one of the most well-known herbs used in the treatment of cataracts in China. However, the potential mechanisms of its anticataract effects have not been fully explored. In this study, network pharmacology was used to investigate the potential mechanism underlying the actions of CS against cataracts, and molecular docking was performed to analyze the binding activity of proteins and compounds. qPCR was performed to detect the mRNA level of genes, and the cell apoptotic rate was measured using flow cytometry. We identified 13 active compounds from CS and 105 targets, as well as 238 cataract-related targets. PPI networks were constructed, and fifty key targets were obtained. These key targets were enriched in the regulation of transcription, apoptotic process, and signal transduction pathways. Molecular docking demonstrated that the compounds of CS exhibited good affinity to some critical targets. Furthermore, CS prevented the apoptosis of human lens epithelial cells induced by UVB lights by decreasing the gene expression of CASP3, ESR1, and TP53 and increasing the CRYAB gene expression. The present study attempted to explain the mechanisms for the effects of CS in the prevention and treatment of cataracts and provided an effective strategy to investigate active ingredients from natural medicines. Further studies are required to verify these findings via in vivo and in vitro experiments.
Copyright © 2022 Ying Zhong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
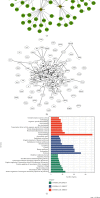
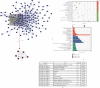
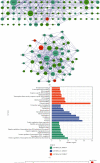


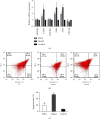
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

