Animal Models and Pathogenesis of Ulcerative Colitis
- PMID: 35860188
- PMCID: PMC9293489
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5927384
Animal Models and Pathogenesis of Ulcerative Colitis
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Animal Models and Pathogenesis of Ulcerative Colitis.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jun 28;2023:9878915. doi: 10.1155/2023/9878915. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37416187 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a kind of inflammatory bowel disease which is needed to be predicted.
Objective: To analyze various animal models of UC conditions and summarizes the animal selection, model progression, and pathogenic mechanisms of UC animal models.
Methods: We surveyed the research papers published in PubMed, Google Scholar, Baidu Scholar, CNKI, SciFinder, and Web of Science in the past 5 years and discussed the experimental animals, modeling methods, and pathogenic mechanisms.
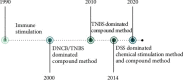
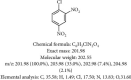
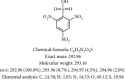
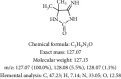
Results: In the selection of experimental animals, rats are considered the best experimental animals. The mainstream modeling methods can be categorized into the chemical stimulation method, immune stimulation method, and compound method, among which the compound method is the most successful. In the study of the pathogenesis of UC, the pathogenesis of UC is due to various pathogenic factors, such as nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandins (PG), proinflammatory factors (IL, TNF-α), and intestinal flora.
Conclusion: The method of building an animal model of UC is well-established, providing a more targeted selection of animal models for future related experiments.
Copyright © 2022 Xin Gao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Chen Z. S., Zhang Z. Q., Nie Z. W. Duplication of animal model of ulcerative colitis and studies on rehabilitation effect of jianpiling prescription. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine . 1990;10(8):488–490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

