Increased Development of Th1, Th17, and Th1.17 Cells Under T1 Polarizing Conditions in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
- PMID: 35860254
- PMCID: PMC9290377
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.848168
Increased Development of Th1, Th17, and Th1.17 Cells Under T1 Polarizing Conditions in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Abstract
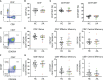
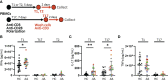
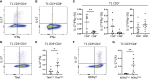
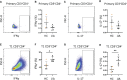
In juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) inflammatory T cells and their produced cytokines are drug targets and play a role in disease pathogenesis. Despite their clinical importance, the sources and types of inflammatory T cells involved remain unclear. T cells respond to polarizing factors to initiate types of immunity to fight infections, which include immunity types 1 (T1), 2 (T2), and 3 (T17). Polarizing factors drive CD4+ T cells towards T helper (Th) cell subtypes and CD8+ T cells towards cytotoxic T cell (Tc) subtypes. T1 and T17 polarization are associated with autoimmunity and production of the cytokines IFNγ and IL-17 respectively. We show that JIA and child healthy control (HC) peripheral blood mononuclear cells are remarkably similar, with the same frequencies of CD4+ and CD8+ naïve and memory T cell subsets, T cell proliferation, and CD4+ and CD8+ T cell subsets upon T1, T2, and T17 polarization. Yet, under T1 polarizing conditions JIA cells produced increased IFNγ and inappropriately produced IL-17. Under T17 polarizing conditions JIA T cells produced increased IL-17. Gene expression of IFNγ, IL-17, Tbet, and RORγT by quantitative PCR and RNA sequencing revealed activation of immune responses and inappropriate activation of IL-17 signaling pathways in JIA polarized T1 cells. The polarized JIA T1 cells were comprised of Th and Tc cells, with Th cells producing IFNγ (Th1), IL-17 (Th17), and both IFNγ-IL-17 (Th1.17) and Tc cells producing IFNγ (Tc1). The JIA polarized CD4+ T1 cells expressed both Tbet and RORγT, with higher expression of the transcription factors associated with higher frequency of IL-17 producing cells. T1 polarized naïve CD4+ cells from JIA also produced more IFNγ and more IL-17 than HC. We show that in JIA T1 polarization inappropriately generates Th1, Th17, and Th1.17 cells. Our data provides a tool for studying the development of heterogeneous inflammatory T cells in JIA under T1 polarizing conditions and for identifying pathogenic immune cells that are important as drug targets and diagnostic markers.
Keywords: T cell; T helper cell (Th); Th1 polarization; Th1.17; Th17; interferon gamma (IFNγ); interleukin 17 (IL-17); juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA).
Copyright © 2022 Patrick, Shoaff, Esmond, Patrick, Flaherty, Graham, Crooke, Thompson and Aune.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aberrant Naive CD4-Positive T Cell Differentiation in Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Committed to B Cell Help.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023 May;75(5):826-841. doi: 10.1002/art.42409. Epub 2023 Mar 17. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36409585
-
Innate Lymphoid Cells and T Cells Contribute to the Interleukin-17A Signature Detected in the Synovial Fluid of Patients With Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Mar;71(3):460-467. doi: 10.1002/art.40731. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30350355 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of the transient nature of the Th17 phenotype of CD4+CD161+ T cells in the synovial fluid of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Aug;63(8):2504-15. doi: 10.1002/art.30332. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. PMID: 21381000
-
A cellular and molecular view of T helper 17 cell plasticity in autoimmunity.J Autoimmun. 2018 Feb;87:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2017.12.007. Epub 2017 Dec 22. J Autoimmun. 2018. PMID: 29275836 Review.
-
The pathogenesis of oligoarticular/polyarticular vs systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis.Autoimmun Rev. 2011 Jun;10(8):482-9. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2011.02.001. Epub 2011 Feb 12. Autoimmun Rev. 2011. PMID: 21320644 Review.
Cited by
-
The immunosuppressive effects and mechanisms of loureirin B on collagen-induced arthritis in rats.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 24;14:1094649. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1094649. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37168850 Free PMC article.
-
Th17/1 and ex-Th17 cells are detected in patients with polyarticular juvenile arthritis and increase following treatment.Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2024 Mar 2;22(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12969-024-00965-5. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2024. PMID: 38431635 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the shared gene signatures of polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis and autoimmune uveitis.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 8;14:1048598. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1048598. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36969183 Free PMC article.
-
Children with extended oligoarticular and polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis have alterations in B and T follicular cell subsets in peripheral blood and a cytokine profile sustaining B cell activation.RMD Open. 2023 Aug;9(3):e002901. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002901. RMD Open. 2023. PMID: 37652558 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical and experimental treatment of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2023 Oct 13;213(3):276-287. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxad045. Clin Exp Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37074076 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

