TLR7 Activation Accelerates Cardiovascular Pathology in a Mouse Model of Lupus
- PMID: 35860280
- PMCID: PMC9289616
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.914468
TLR7 Activation Accelerates Cardiovascular Pathology in a Mouse Model of Lupus
Abstract
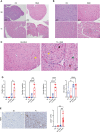
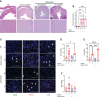
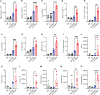
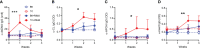
We report a novel model of lupus-associated cardiovascular pathology accelerated by the TLR7 agonist R848 in lupus-prone B6.Sle1.Sle2.Sle3 (TC) mice. R848-treated TC mice but not non-autoimmune C57BL/6 (B6) controls developed microvascular inflammation and myocytolysis with intracellular vacuolization. This histopathology was similar to antibody-mediated rejection after heart transplant, although it did not involve complement. The TC or B6 recipients of serum or splenocytes from R848-treated TC mice developed a reactive cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, which also presents spontaneously in old TC mice as well as in TC.Rag-/- mice that lack B and T cells. Each of these cardiovascular lesions correspond to abnormalities that have been reported in lupus patients. Lymphoid and non-lymphoid immune cells as well as soluble factors contribute to lupus-associated cardiovascular lesions in TC mice, which can now be dissected using this model with and without R848 treatment.
Keywords: TLR7; autoimmunity; cardiovascular disease; lupus; mouse models.
Copyright © 2022 Elshikha, Teng, Kanda, Li, Choi, Abboud, Terrell, Fredenburg and Morel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Puntmann VO, D'Cruz D, Smith Z, Pastor A, Choong P, Voigt T, et al. Native Myocardial T1 Mapping by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Subclinical Cardiomyopathy in Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Circulation Cardiovasc Imaging (2013) 6:295–301. doi: 10.1161/circimaging.112.000151 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

