Association of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms of rs2383206, rs2383207, and rs10757278 With Stroke Risk in the Chinese Population: A Meta-analysis
- PMID: 35860475
- PMCID: PMC9291403
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.905619
Association of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms of rs2383206, rs2383207, and rs10757278 With Stroke Risk in the Chinese Population: A Meta-analysis
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Association of single-nucleotide polymorphisms of rs2383206, rs2383207, and rs10757278 with stroke risk in the Chinese population: A meta-analysis.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 10;13:980218. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.980218. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36299594 Free PMC article.
Abstract
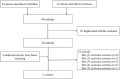
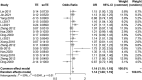
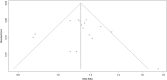
Several studies have reported that chromosome 9p21 is significantly associated with ischemic stroke (IS) risk, with the G allele associated with increased risk. However, controversial results have been reported in the literature. We systematically assessed the relationship between stroke and three 9p21 loci (rs2303206, rs2383207, and rs10757278) in this meta-analysis. First, we searched the PubMed and Embase databases for relevant studies. We then calculated odds ratios using the chi-squared test. The evaluation of experimental data was performed using bias tests and sensitivity analyses. We analyzed data from 16 studies involving 18,584 individuals of Chinese ancestry, including 14,033 cases and 14,656 controls. Our results indicated that chromosome 9p21 is significantly associated with IS (odds ratio: 1.15, 95% confidence interval: 1.1-1.20, p < 0.0001). Because the three single-nucleotide polymorphisms (rs2383206, rs2383207, and 10757278) have a linkage disequilibrium relationship, all three may increase the risk of IS.
Keywords: Chinese; chromosome 9p21; ischemic stroke; rs10757278; rs2383206; rs2383207.
Copyright © 2022 Hu, Wang, Cui and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Genetic variants on chromosome 9p21 confer risks of cerebral infarction in the Chinese population: a meta-analysis.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2019 Jan-Dec;33:2058738419847852. doi: 10.1177/2058738419847852. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31055994 Free PMC article.
-
Corrigendum: Association of single-nucleotide polymorphisms of rs2383206, rs2383207, and rs10757278 with stroke risk in the Chinese population: A meta-analysis.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 10;13:980218. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.980218. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36299594 Free PMC article.
-
The cardiovascular implication of single nucleotide polymorphisms of chromosome 9p21 locus among Arab population.J Res Med Sci. 2015 Apr;20(4):346-52. J Res Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26109989 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of ANRIL polymorphisms on the likelihood of coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Apr;120(4):6113-6119. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27898. Epub 2018 Nov 1. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30387168 Review.
-
Associations Between Common Polymorphisms of CDKN2B-AS and Susceptibility to ASCVD.Angiology. 2020 Nov;71(10):934-941. doi: 10.1177/0003319720941387. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Angiology. 2020. PMID: 32696678
References
-
- Akinyemi R., Arnett D. K., Tiwari H. K., Ovbiagele B., Sarfo F., Srinivasasainagendra V., et al. (2017). Interleukin-6 (IL-6) rs1800796 and Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor (CDKN2A/CDKN2B) rs2383207 are Associated with Ischemic Stroke in Indigenous West African Men. J. Neurological Sci. 379, 229–235. 10.1016/j.jns.2017.05.046 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dehghan A., Bis J. C., White C. C., Smith A. V., Morrison A. C., Cupples L. A., et al. (2016). Genome-Wide Association Study for Incident Myocardial Infarction and Coronary Heart Disease in Prospective Cohort Studies: The CHARGE Consortium. PLoS One 11, e0144997. 10.1371/journal.pone.0144997 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

