Predicting 30-Day Readmission for Stroke Using Machine Learning Algorithms: A Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 35860493
- PMCID: PMC9289395
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.875491
Predicting 30-Day Readmission for Stroke Using Machine Learning Algorithms: A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Machine learning algorithms for predicting 30-day stroke readmission are rarely discussed. The aims of this study were to identify significant predictors of 30-day readmission after stroke and to compare prediction accuracy and area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve in five models: artificial neural network (ANN), K nearest neighbor (KNN), random forest (RF), support vector machine (SVM), naive Bayes classifier (NBC), and Cox regression (COX) models.
Methods: The subjects of this prospective cohort study were 1,476 patients with a history of admission for stroke to one of six hospitals between March, 2014, and September, 2019. A training dataset (n = 1,033) was used for model development, and a testing dataset (n = 443) was used for internal validation. Another 167 patients with stroke recruited from October, to December, 2019, were enrolled in the dataset for external validation. A feature importance analysis was also performed to identify the significance of the selected input variables.
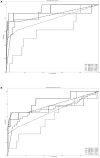
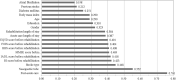
Results: For predicting 30-day readmission after stroke, the ANN model had significantly (P < 0.001) higher performance indices compared to the other models. According to the ANN model results, the best predictor of 30-day readmission was PAC followed by nasogastric tube insertion and stroke type (P < 0.05). Using a machine learning ANN model to obtain an accurate estimate of 30-day readmission for stroke and to identify risk factors may improve the precision and efficacy of management for these patients.
Conclusion: Using a machine-learning ANN model to obtain an accurate estimate of 30-day readmission for stroke and to identify risk factors may improve the precision and efficacy of management for these patients. For stroke patients who are candidates for PAC rehabilitation, these predictors have practical applications in educating patients in the expected course of recovery and health outcomes.
Keywords: 30-day readmission; artificial neural network; feature importance analysis; post-acute care; stroke.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Chung, Yeh, Lou, Lin, Lin, Hsien, Hung, Yeh and Shi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and internal validation of a machine-learning-developed model for predicting 1-year mortality after fragility hip fracture.BMC Geriatr. 2022 May 24;22(1):451. doi: 10.1186/s12877-022-03152-x. BMC Geriatr. 2022. PMID: 35610589 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing readmission prediction model in older stroke patients by integrating insight from readiness for hospital discharge: Prospective cohort study.Int J Med Inform. 2025 May;197:105845. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2025.105845. Epub 2025 Feb 22. Int J Med Inform. 2025. PMID: 40015152
-
Predicting clinically significant motor function improvement after contemporary task-oriented interventions using machine learning approaches.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2020 Sep 29;17(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12984-020-00758-3. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2020. PMID: 32993692 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting all-cause 90-day hospital readmission for dental patients using machine learning methods.BDJ Open. 2021 Jan 22;7(1):1. doi: 10.1038/s41405-021-00057-6. BDJ Open. 2021. PMID: 33483463 Free PMC article.
-
The most efficient machine learning algorithms in stroke prediction: A systematic review.Health Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 1;7(10):e70062. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70062. eCollection 2024 Oct. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39355095 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prediction Models for Post-Stroke Hospital Readmission: A Systematic Review.Public Health Nurs. 2025 Jan-Feb;42(1):535-546. doi: 10.1111/phn.13441. Epub 2024 Oct 14. Public Health Nurs. 2025. PMID: 39402856 Free PMC article.
-
An exploration on the machine-learning-based stroke prediction model.Front Neurol. 2024 Apr 29;15:1372431. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1372431. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38742047 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Machine Learning and Traditional Statistical Models to Assess the Value of Stroke Genetic Liability for Prediction of Risk of Stroke Within the UK Biobank.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Apr 26;13(9):1003. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13091003. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361781 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning-based survival models for predicting rehospitalization of older hip fracture patients: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 May 8;26(1):451. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08710-z. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40340665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liotta EM, Singh M, Kosteva AR, Beaumont JL, Guth JC, Bauer RM, et al. . Predictors of 30 day readmission after intracerebral hemorrhage: a single-center approach for identifying potentially modifiable associations with readmission. Crit Care Med. (2013) 41:2762–9. 10.1097/CCM.0b013e318298a10f - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amin A, Deitelzweig S, Bucior I, Lin J, Lingohr-Smith M, Menges B, et al. . Frequency of hospital readmissions for venous thromboembolism and associated hospital costs and length of stay among acute medically ill patients in the US. J Med Econ. (2019) 22:1119–25. 10.1080/13696998.2019.1618862 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

