Emerging High-Frequency Ultrasound Imaging in Medical Cosmetology
- PMID: 35860664
- PMCID: PMC9289277
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.885922
Emerging High-Frequency Ultrasound Imaging in Medical Cosmetology
Abstract
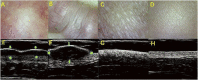
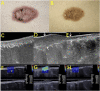
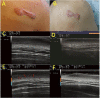
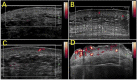
Cosmetic skin diseases are a part of many dermatological concerns brought up by patients, which negatively affect mental health and quality of life. Imaging technology has an established role in the diagnosis of cosmetic skin diseases by recognizing information on deep skin lesions. Due to the complex physiological and pathological nature of cosmetic skin diseases, the diagnostic imaging performance varies greatly. Developing noninvasive technology models with wide applicability, particularly high-frequency ultrasound (HFUS), which is able to achieve high-resolution imaging of the skin from the stratum corneum down to the deep fascia, is of great significance to medical cosmetology. To explore the great potential of HFUS in cosmetic skin diseases, a narrative review of literature from PubMed and Web of Science published between 1985 and 2022 was conducted. This narrative review focuses on the progression of HFUS imaging in medical cosmetology, especially on its promising application in the quantitative evaluation and differential diagnosis of cutaneous pathological scar, port wine stain (PWS), acne, skin aging, and other cosmetic applications.
Keywords: dermatology; high-frequency ultrasound; medical cosmetology; pathological scar; port wine stain.
Copyright © 2022 Tao, Wei, Su, Hu and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
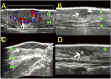
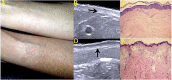
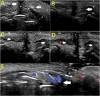
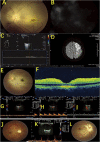
References
-
- Ardigo M., Cameli N., Berardesca E., Gonzalez S. (2010). Characterization and Evaluation of Pigment Distribution and Response to Therapy in Melasma Using In Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy: a Preliminary Study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol Venereol. 24 (11), 1296–1303. 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03633.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

