Investigation of genetic polymorphism of Russian rape and turnip rape varieties using SSR and SRAP markers
- PMID: 35860676
- PMCID: PMC9259662
- DOI: 10.18699/VJGB-22-42
Investigation of genetic polymorphism of Russian rape and turnip rape varieties using SSR and SRAP markers
Abstract
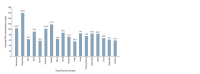
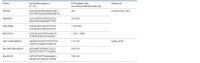
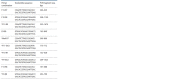
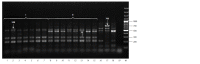
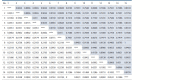
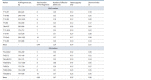
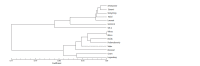
Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) and turnip rape (B. rapa L. subsp. campestris (L.)) are important agricultural plants widely used for food, fodder and technical purposes and as green manure. Over the past decades, a large number of perspective varieties that are being currently cultivated in every region of Russia have been developed. To increase the breeding eff iciency and facilitate the seed production, modern molecular-genetic techniques should be introduced as means to estimate species and varietal diversity. The objective of the presented research study was to investigate DNA polymorphism of the rapeseed and turnip rape varieties developed at Federal Williams Research Center of Forage Production and Agroecology and detect informative markers for varietal identif ication and genetic certif ication. To genotype 18 gDNA samples, 42 and 25 combinations of respective SSR and SRAP primers were used. The results obtained demonstrate that SRAP markers were more effective for polymorphism analysis: 36 % of the tested markers revealed genetic polymorphism compared with only 16.7 % of microsatellite loci. Molecular markers to detect differences at interspecif ic and intervarietal levels have also been found. For the investigated set, such microsatellite loci as Na12A02, Ni2C12, Ni02-D08a, Ra02-E01, Ni03H07а and SRAP-marker combinations as F13-R9, Me4- R7, F11-Em2, F10-R7, F9-Em2 and F9-R8 proved to be informative. Application of the two marker techniques made it possible to detect a higher level of DNA polymorphism in plants of different types (spring and winter varieties) if compared against the intervarietal differences within a species or a group. According to Nei's genetic diversity index, in the cluster of winter rapeseed, VIK 2 and Gorizont varieties had the longest genetic distance, and in the spring cluster, these were Novosel and Veles. A high level of similarity was found between Vikros and Bizon winter rapeseed varieties. The results obtained have a high practical value for varietal specif ication of seed material and genetic certif ication of rapeseed and turnip rape varieties.
Рапс (Brassica napus L.) и сурепица (B. rapa L. subsp. campestris (L.)) – важные сельскохозяйственные культуры, широко используются для продовольственных, кормовых и технических целей, а также в качестве сидератов. За последние десятилетия создано большое количество перспективных сортов, культивируемых практически во всех регионах России. Для повышения эффективности селекционного процесса и успешного развития семеноводства необходимо внедрять современные молекулярно-генетические методы оценки видового и сортового разнообразия. Цель настоящей работы заключалась в изучении ДНК-полиморфизма сортов рапса и сурепицы селекции Федерального научного центра кормопроизводства и агроэкологии им. В.Р. Вильямса и выявлении информативных маркеров для сортовой идентификации и генетической паспортизации. Для генотипирования 18 образцов геномной ДНК использовали 42 и 25 комбинаций SSR- и SRAP-праймеров соответственно. Результаты показали, что маркеры SRAP более эффективны для анализа полиморфизма изучаемого материала: 36 % от общего числа испытанных маркеров демонстрировали генетический полиморфизм, тогда как для микросателлитных локусов этот показатель равнялся 16.7 %. Определены молекулярные маркеры для выявления различий на межвидовом и межсортовом уровнях. Информативными для исследуемой выборки сортов оказались микросателлитные локусы Na12A02, Ni2C12, Ni02-D08a, Ra02-E01, Ni03H07а и комбинации SRAP-маркеров F13-R9, Me4-R7, F11-Em2, F10-R7, F9-Em2 и F9-R8. Анализ сортового материала по двум системам маркирования показал более высокий уровень ДНК-полиморфизма у образцов растений разного типа развития (яровой/озимый) в сравнении с различиями между сортами в пределах вида или группы. Согласно индексам генетического разнообразия Нея, в кластере сортов озимого рапса наибольшей генетической удаленностью выделялись ВИК 2 и Горизонт, среди яровых – Новосёл и Велес. Высокий уровень сходства обнаружен между яровыми сортами рапса Викрос и Бизон. Полученная информация имеет практическое значение для контроля сортовой принадлежности и генетической паспортизации семенного материала сортов рапса и сурепицы.
Keywords: B. rapa L. campestris; Brassica napus L.; SRAP markers; SSR markers; bulk samples; forage crops; genetic polymorphism.
Copyright © AUTHORS.
Figures

LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
