Enhancing and inhibitory motifs regulate CD4 activity
- PMID: 35861317
- PMCID: PMC9333989
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.79508
Enhancing and inhibitory motifs regulate CD4 activity
Abstract
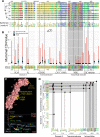
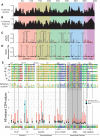
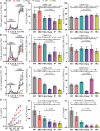
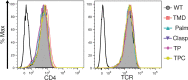
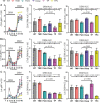
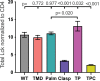
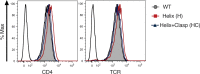
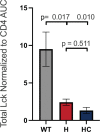
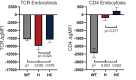
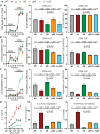
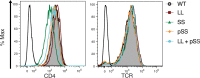
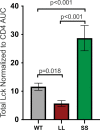
CD4+ T cells use T cell receptor (TCR)-CD3 complexes, and CD4, to respond to peptide antigens within MHCII molecules (pMHCII). We report here that, through ~435 million years of evolution in jawed vertebrates, purifying selection has shaped motifs in the extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular domains of eutherian CD4 that enhance pMHCII responses, and covary with residues in an intracellular motif that inhibits responses. Importantly, while CD4 interactions with the Src kinase, Lck, are viewed as key to pMHCII responses, our data indicate that CD4-Lck interactions derive their importance from the counterbalancing activity of the inhibitory motif, as well as motifs that direct CD4-Lck pairs to specific membrane compartments. These results have implications for the evolution and function of complex transmembrane receptors and for biomimetic engineering.
Keywords: CD4; T cell; TCR; activation; evolution; evolutionary biology; immunology; inflammation; mouse; signaling.
© 2022, Lee et al.
Conflict of interest statement
ML, PT, CK, KL, HP, KV No competing interests declared, MK has disclosed an outside interest in Module Therapeutics to the University of Arizona. Conflicts of interest resulting from this interest are being managed by the University of Arizona in accordance with their policies
Figures









Similar articles
-
The CD4 transmembrane GGXXG and juxtamembrane (C/F)CV+C motifs mediate pMHCII-specific signaling independently of CD4-LCK interactions.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 29:2023.05.05.539613. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.05.539613. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Elife. 2024 Apr 19;12:RP88225. doi: 10.7554/eLife.88225. PMID: 37214965 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The CD4 transmembrane GGXXG and juxtamembrane (C/F)CV+C motifs mediate pMHCII-specific signaling independently of CD4-LCK interactions.Elife. 2024 Apr 19;12:RP88225. doi: 10.7554/eLife.88225. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38639990 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal TCR-CD3 and CD4 Engagement of a Nucleating pMHCII Stabilizes a Functional Receptor Macrocomplex.Cell Rep. 2018 Jan 30;22(5):1263-1275. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.12.104. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29386113 Free PMC article.
-
CD4 and signal transduction.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1996;205:47-62. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-79798-9_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8575197 Review.
-
CD4, CD8 and the TCR-CD3 complex: a novel class of protein-tyrosine kinase receptor.Immunol Today. 1990 Nov;11(11):400-6. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90159-7. Immunol Today. 1990. PMID: 1964053 Review.
Cited by
-
The CD4 transmembrane GGXXG and juxtamembrane (C/F)CV+C motifs mediate pMHCII-specific signaling independently of CD4-LCK interactions.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 29:2023.05.05.539613. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.05.539613. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Elife. 2024 Apr 19;12:RP88225. doi: 10.7554/eLife.88225. PMID: 37214965 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The CD4 transmembrane GGXXG and juxtamembrane (C/F)CV+C motifs mediate pMHCII-specific signaling independently of CD4-LCK interactions.Elife. 2024 Apr 19;12:RP88225. doi: 10.7554/eLife.88225. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38639990 Free PMC article.
-
The TCR Cα Domain Regulates Responses to Self-pMHC Class II.J Immunol. 2022 Nov 15;209(10):2033-2041. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200377. J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36426940 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

