Assessment of Compound-Specific Fatty Acid δ13C and δ2H Values to Track Fish Mobility in a Small Sub-alpine Catchment
- PMID: 35861449
- PMCID: PMC9352314
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.2c02089
Assessment of Compound-Specific Fatty Acid δ13C and δ2H Values to Track Fish Mobility in a Small Sub-alpine Catchment
Abstract
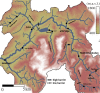
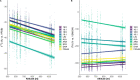
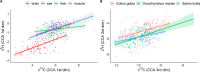
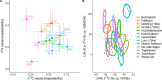
Methods for identifying origin, movement, and foraging areas of animals are essential for understanding ecosystem connectivity, nutrient flows, and other ecological processes. Telemetric methods can provide detailed spatial coverage but are limited to a minimum body size of specimen for tagging. In recent years, stable isotopes have been increasingly used to track animal migration by linking landscape isotope patterns into movement (isoscapes). However, compared to telemetric methods, the spatial resolution of bulk stable isotopes is low. Here, we examined a novel approach by evaluating the use of compound-specific hydrogen and carbon stable isotopes of fatty acids (δ2HFA and δ13CFA) from fish liver, muscle, brain, and eye tissues for identifying site specificity in a 254 km2 sub-alpine river catchment. We analyzed 208 fish (European bullhead, rainbow trout, and brown trout) collected in 2016 and 2018 at 15 different sites. δ13CFA values of these fish tissues correlated more among each other than those of δ2HFA values. Both δ2HFA and δ13CFA values showed tissue-dependent isotopic fractionation, while fish taxa had only small effects. The highest site specificity was for δ13CDHA values, while the δ2H isotopic difference between linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid resulted in the highest site specificity. Using linear discrimination analysis of FA isotope values, over 90% of fish could be assigned to their location of origin; however, the accuracy dropped to about 56% when isotope data from 2016 were used to predict the sites for samples collected in 2018, suggesting temporal shifts in site specificity of δ2HFA and δ13CFA. However, the predictive power of δ2HFA and δ13CFA over this time interval was still higher than site specificity of bulk tissue isotopes for a single time point. In summary, compound-specific isotope analysis of fatty acids may become a highly effective tool for assessing fine and large-scale movement and foraging areas of animals.
Keywords: carbon stable isotopes; compound-specific isotope analysis; fatty acids; fish migration; hydrogen stable isotopes; site specificity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Compound-specific stable isotope analyses of fatty acids indicate feeding zones of zooplankton across the water column of a subalpine lake.Oecologia. 2024 Jun;205(2):325-337. doi: 10.1007/s00442-024-05574-3. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Oecologia. 2024. PMID: 38829405 Free PMC article.
-
Diet-tissue discrimination factors and turnover of carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes in tissues of an adult predatory coral reef fish, Plectropomus leopardus.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2016 Jan 15;30(1):29-44. doi: 10.1002/rcm.7406. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2016. PMID: 26661968
-
Fish scale stable isotopes as potential indicators of nutrient pollution: Exploring the response of roach (Rutilus rutilus) scale δ15N and δ13C to a gradient of land use disturbance.Sci Total Environ. 2023 Mar 20;865:161198. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.161198. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 36592901
-
Differentiating wild from captive animals: an isotopic approach.PeerJ. 2023 Nov 24;11:e16460. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16460. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 38025752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Why aquatic scientists should use sulfur stable isotope ratios (ẟ34S) more often.Chemosphere. 2024 May;355:141816. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.141816. Epub 2024 Mar 29. Chemosphere. 2024. PMID: 38556184 Review.
Cited by
-
Compound-specific stable isotope analyses of fatty acids indicate feeding zones of zooplankton across the water column of a subalpine lake.Oecologia. 2024 Jun;205(2):325-337. doi: 10.1007/s00442-024-05574-3. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Oecologia. 2024. PMID: 38829405 Free PMC article.
-
Protocols for sample preparation and compound-specific stable-isotope analyses (δ2H, δ13C) of fatty acids in biological and environmental samples.MethodsX. 2023 Jul 8;11:102283. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2023.102283. eCollection 2023 Dec. MethodsX. 2023. PMID: 38098777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilkes M. A.; Webb J. A.; Pompeu P. S.; Silva L. G. M.; Vowles A. S.; Baker C. F.; Franklin P.; Link O.; Habit E.; Kemp P. S. Not Just a Migration Problem: Metapopulations, Habitat Shifts, and Gene Flow Are Also Important for Fishway Science and Management. River Res. Appl. 2019, 35, 1688–1696. 10.1002/rra.3320. - DOI
-
- Burtner A. M.; McIntyre P. B.; Allan J. D.; Kashian D. R. The Influence of Land Use and Potamodromous Fish on Ecosystem Function in Lake Superior Tributaries. J. Great Lake. Res. 2011, 37, 521–527. 10.1016/j.jglr.2011.05.014. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

