The burden of alcoholic cardiomyopathy in China and different regions around the world
- PMID: 35861492
- PMCID: PMC9304924
- DOI: 10.7189/jogh.12.04041
The burden of alcoholic cardiomyopathy in China and different regions around the world
Abstract
Background: Alcoholic cardiomyopathy (ACM) remains a significant public health issue with a growing global burden. The burden of ACM in China and different regions remains poorly understood.
Methods: Data on ACM deaths, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), the corresponding global age-standardized death rate (ASDR), age-standardized DALY rate and estimated annual percentage change (EAPC) were analysed based on age, sex, socio-demographic index (SDI) quintiles, different regions and in China from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study 2019.
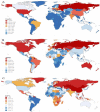
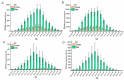
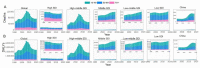
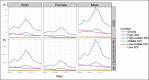
Results: Globally, the death rate and DALYs due to ACM were 71 723 and 2 441 108 in 2019, 33.06% and 38.79% increase from 1990, respectively. The corresponding ASDR and age-standardized DALY rate decreased with EAPC of -1.52 (95% uncertainty interval (UI) = -2.39, -0.65) and -1.12 (95% UI = -2.14, -0.10). The high-middle SDI regions, especially Eastern Europe, showed the highest number of ACM-related deaths and DALYs. The ACM-related deaths and DALYs were 2545 and 87823 in China in 2019, 171.03% and 147.17% increase from 1990, respectively. Unlike the world level, ASDR and age-standardized DALY rate also increased in China. The ACM burden is higher in men, and people with 50 to 69 years old accounted for the most.
Conclusions: ACM burden in China and across the world increased substantially from 1990 to 2019. The greatest burden was borne by the high-middle SDI regions, especially by men aged 50-69 years old. Geographically and gender-age tailored strategies were needed to prevent ACM.
Copyright © 2022 by the Journal of Global Health. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors completed the ICMJE Declaration of Interest Form (available upon request from the corresponding author), and declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Herz MDT.Ein Beitrag zur Lehre von der Überanstrengung des Herzens. Dtsch Arch Klin Med. 2013;19:449.
-
- Kozlovskiĭ IV.Early and progressing alcohol cardiomyopathy. Klin Med (Mosk). 2007;85:51-4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
