Effect of canagliflozin on the decline of estimated glomerular filtration rate in chronic kidney disease patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, phase III study in Japan
- PMID: 35861630
- PMCID: PMC9720226
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.13888
Effect of canagliflozin on the decline of estimated glomerular filtration rate in chronic kidney disease patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, phase III study in Japan
Abstract
Aims/introduction: The Canagliflozin and Renal Events in Diabetes with Established Nephropathy Clinical Evaluation (CREDENCE) trial has shown the effects of canagliflozin on preventing clinically important kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease; however, not many Japanese patients were included in the trial. The present study evaluated the efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in Japanese chronic kidney disease patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
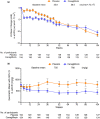
Materials and methods: In this multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, phase III study, chronic kidney disease patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were randomly assigned to receive either 100 mg canagliflozin or a matching placebo once daily for 104 weeks. The primary efficacy end-point was the incidence of a 30% decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate.
Results: Overall, 308 patients were randomized to the canagliflozin (n = 154) and placebo (n = 154) groups. The incidence of a 30% decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate at week 104 was 18.2% and 29.5%, respectively, and the point estimate of the intergroup difference (placebo - canagliflozin) was 11.3% (95% confidence interval 1.2-21.5, P = 0.029), which was significant. The overall incidence of adverse events was similar in the two groups.
Conclusions: This study suggests that canagliflozin safely reduces the risk of end-stage renal disease in Japanese chronic kidney disease patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: Canagliflozin; Chronic kidney disease; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, et al. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 1296–1305. - PubMed
-
- Imai E, Horio M, Watanabe T, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the Japanese general population. Clin Exp Nephrol 2009; 13: 621–630. - PubMed
-
- End Stage Renal Disease: Chapter 11. Available from: https://adr.usrds.org/2020/end‐stage‐renal‐disease/11‐international‐comp... Accessed December 03, 2021.
-
- The data provided by the Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy. Available from: https://docs.jsdt.or.jp/overview/file/2020/pdf/03.pdf Accessed February 23, 2022.
-
- Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2019; 380: 2295–2306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

