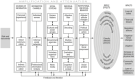
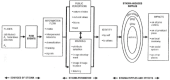
The social amplification of risk framework: New perspectives
- PMID: 35861634
- PMCID: PMC10360138
- DOI: 10.1111/risa.13926
The social amplification of risk framework: New perspectives
Abstract
Several decades have elapsed since the introduction in 1988 of the social amplification of risk framework (SARF) by researchers from Clark University and Decision Research. SARF was offered as an umbrella under which social, psychological, and cultural theories of risk could be integrated and thereby supplement technical risk analyses. Some critics suggest that SARF cannot be tested thus, the framework is useful, at most, as a post hoc analysis of some kinds of risks. Others counter that predictability is not required for a framework to be useful and that SARF is an effective tool in organizing data related to public perceptions, values, and behaviors. It can also be used to design more effective risk communication and public engagement strategies. SARF also suggests how to conceptually view the dynamics of social media channels, despite the fact that SARF was developed before the explosion of global digital platforms. The papers in this special issue consider developments, refinements, critiques, contributions, extensions of the approach to new risk issues, as well as the findings and hypotheses that have grown out of what is now close to three decades of empirical research. This introductory paper provides background on SARF, presents a literature review since 2003, introduces the contributions to this issue, and highlights several areas for future research.
© 2022 Society for Risk Analysis.
Figures
References
-
- Arvai, J. , & Rivers, L. I. I. I. (2014). Effective risk communication. Earthscan.
-
- Brown, A. (2021). Understanding the technical and societal relationship between shadow banning and algorithmic bias. Forbes, https://www.forbes.com/sites/anniebrown/2021/10/27/understanding‐the‐tec...
-
- Burns, W. J. , Slovic, P. , Kasperson, R. E. , Kasperson, J. X. , Renn, O. , & Emani, S. (1993). Incorporating structural models into research on the social amplification of risk: Implications for theory construction and decision making. Risk Analysis, 13(6), 611–624.
-
- Busby, J. , & Duckett, D. (2012). Social risk amplification as an attribution: The case of zoonotic disease outbreaks. Journal of Risk Research, 15(9), 1049–1074.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources