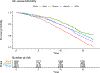
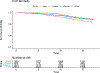
Racial and Ethnic Differences in All-Cause and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality: The MESA Study
- PMID: 35861763
- PMCID: PMC9937428
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.059174
Racial and Ethnic Differences in All-Cause and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality: The MESA Study
Abstract
Background: Despite improvements in population health, marked racial and ethnic disparities in longevity and cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality persist. This study aimed to describe risks for all-cause and CVD mortality by race and ethnicity, before and after accounting for socioeconomic status (SES) and other factors, in the MESA study (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis).
Methods: MESA recruited 6814 US adults, 45 to 84 years of age, free of clinical CVD at baseline, including Black, White, Hispanic, and Chinese individuals (2000-2002). Using Cox proportional hazards modeling with time-updated covariates, we evaluated the association of self-reported race and ethnicity with all-cause and adjudicated CVD mortality, with progressive adjustments for age and sex, SES (neighborhood SES, income, education, and health insurance), lifestyle and psychosocial risk factors, clinical risk factors, and immigration history.
Results: During a median of 15.8 years of follow-up, 22.8% of participants (n=1552) died, of which 5.3% (n=364) died of CVD. After adjusting for age and sex, Black participants had a 34% higher mortality hazard (hazard ratio [HR], 1.34 [95% CI, 1.19-1.51]), Chinese participants had a 21% lower mortality hazard (HR, 0.79 [95% CI, 0.66-0.95]), and there was no mortality difference in Hispanic participants (HR, 0.99 [95% CI, 0.86-1.14]) compared with White participants. After adjusting for SES, the mortality HR for Black participants compared with White participants was reduced (HR, 1.16 [95% CI, 1.01-1.34]) but still statistically significant. With adjustment for SES, the mortality hazards for Chinese and Hispanic participants also decreased in comparison with White participants. After further adjustment for additional risk factors and immigration history, Hispanic participants (HR, 0.77 [95% CI, 0.63-0.94]) had a lower mortality risk than White participants, and hazard ratios for Black participants (HR, 1.08 [95% CI, 0.92-1.26]) and Chinese participants (HR, 0.81 [95% CI, 0.60-1.08]) were not significantly different from those of White participants. Similar trends were seen for CVD mortality, although the age- and sex-adjusted HR for CVD mortality for Black participants compared with White participants was greater than all-cause mortality (HR, 1.72 [95% CI, 1.34-2.21] compared with HR, 1.34 [95% CI, 1.19-1.51]).
Conclusions: These results highlight persistent racial and ethnic differences in overall and CVD mortality, largely attributable to social determinants of health, and support the need to identify and act on systemic factors that shape differences in health across racial and ethnic groups.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; ethnic and racial minorities; health status disparities; social determinants of health.
Figures
References
-
- Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, Benjamin EJ, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Cheng S, Delling FN, Elkind MSV, Evenson KR, Ferguson JF, Gupta DK, Khan SS, Kissela BM, Knutson KL, Lee CD, Lewis TT, Liu J, Loop MS, Lutsey PL, Ma J, Mackey J, Martin SS, Matchar DB, Mussolino ME, Navaneethan SD, Perak AM, Roth GA, Samad Z, Satou GM, Schroeder EB, Shah SH, Shay CM, Stokes A, VanWagner LB, Wang NY and Tsao CW. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2021 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143:e254–e743. - PubMed
-
- Carnethon MR, Pu J, Howard G, Albert MA, Anderson CAM, Bertoni AG, Mujahid MS, Palaniappan L, Taylor HA Jr., Willis M and Yancy CW. Cardiovascular Health in African Americans: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017;136:e393–e423. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez CJ, Allison M, Daviglus ML, Isasi CR, Keller C, Leira EC, Palaniappan L, Piña IL, Ramirez SM, Rodriguez B and Sims M. Status of cardiovascular disease and stroke in Hispanics/Latinos in the United States: a science advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2014;130:593–625. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 75N92020D00001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P60 MD002249/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES007033/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071759/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical