Cannabinoids to Improve Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Neurological or Oncological Disease: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35861789
- PMCID: PMC9940814
- DOI: 10.1089/can.2021.0187
Cannabinoids to Improve Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Neurological or Oncological Disease: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Cannabinoids have been suggested to alleviate frequently experienced symptoms of reduced mental well-being such as anxiety and depression. Mental well-being is an important subdomain of health-related quality of life (HRQoL). Reducing symptoms and maintaining HRQoL are particularly important in malignant primary brain tumor patients, as treatment options are often noncurative and prognosis remains poor. These patients frequently report unprescribed cannabinoid use, presumably for symptom relieve. As studies on brain tumor patients specifically are lacking, we performed a meta-analysis of the current evidence on cannabinoid efficacy on HRQoL and mental well-being in oncological and neurological patients. Methods: We performed a systematic PubMed, PsychINFO, Embase, and Web of Science search according to PRISMA guidelines on August 2 and 3, 2021. We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that assessed the effects of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) or cannabidiol (CBD) on general HRQoL and mental well-being. Pooled effect sizes were calculated using Hedges g. Risk of bias of included studies was assessed using Cochrane's Risk of Bias tool. Results: We included 17 studies: 4 in oncology and 13 in central nervous system (CNS) disease. Meta-analysis showed no effect of cannabinoids on general HRQoL (g=-0.02 confidence interval [95% CI -0.11 to 0.06]; p=0.57) or mental well-being (g=-0.02 [95% CI -0.16 to 0.13]; p=0.81). Conclusions: RCTs in patients with cancer or CNS disease showed no effect of cannabinoids on HRQoL or mental well-being. However, studies were clinically heterogeneous and since many glioma patients currently frequently use cannabinoids, future studies are necessary to evaluate its value in this specific population.
Keywords: anxiety; brain tumors; cannabidiol; depression; glioma; Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol.
Conflict of interest statement
Arrieta reports personal fees from Pfizer, grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca, grants and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, personal fees from Lilly, personal fees from Merck, personal fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, and grants and personal fees from Roche, outside the submitted work. The other authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
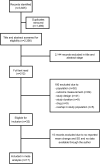
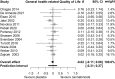
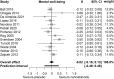


References
-
- Hays RD, Reeve BB. Measurement and modeling of health-related quality of life. In: International Encyclopedia of Public Health. Elsevier Inc.; 2008; pp. 241–252; doi: 10.1016/B978-012373960-5.00336-1. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

