Spatiotemporal regulation of human IFN-ε and innate immunity in the female reproductive tract
- PMID: 35862222
- PMCID: PMC9675573
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.135407
Spatiotemporal regulation of human IFN-ε and innate immunity in the female reproductive tract
Abstract
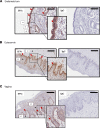
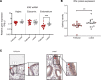
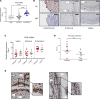
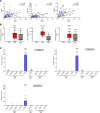
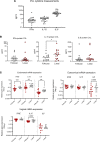
Although published studies have demonstrated that IFN-ε has a crucial role in regulating protective immunity in the mouse female reproductive tract, expression and regulation of IFN-ε in the human female reproductive tract (hFRT) have not been characterized to our knowledge. We obtained hFRT samples from a well-characterized cohort of women to enable us to comprehensively assess ex vivo IFN-ε expression in the hFRT at various stages of the menstrual cycle. We found that among the various types of IFNs, IFN-ε was uniquely, selectively, and constitutively expressed in the hFRT epithelium. It had distinct expression patterns in the surface and glandular epithelia of the upper hFRT compared with basal layers of the stratified squamous epithelia of the lower hFRT. There was cyclical variation of IFN-ε expression in the endometrial epithelium of the upper hFRT and not in the distal FRT, consistent with selective endometrial expression of the progesterone receptor and regulation of the IFNE promoter by progesterone. Because we showed IFN-ε stimulated important protective IFN-regulated genes in FRT epithelium, this characterization is a key element in understanding the mechanisms of hormonal control of mucosal immunity.
Keywords: Cytokines; Immunology; Reproductive Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Wira CR, et al. Sex hormone regulation of innate immunity in the female reproductive tract: the role of epithelial cells in balancing reproductive potential with protection against sexually transmitted pathogens. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2010;63(6):544–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2010.00842.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

