ELF4 is a critical component of a miRNA-transcription factor network and is a bridge regulator of glioblastoma receptor signaling and lipid dynamics
- PMID: 35862252
- PMCID: PMC10013642
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/noac179
ELF4 is a critical component of a miRNA-transcription factor network and is a bridge regulator of glioblastoma receptor signaling and lipid dynamics
Abstract
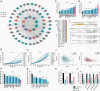
Background: The loss of neurogenic tumor suppressor microRNAs miR-124, miR-128, and miR-137 is associated with glioblastoma's undifferentiated state. Most of their impact comes via the repression of a network of oncogenic transcription factors. We conducted a high-throughput functional siRNA screen in glioblastoma cells and identify E74 like ETS transcription factor 4 (ELF4) as the leading contributor to oncogenic phenotypes.
Methods: In vitro and in vivo assays were used to assess ELF4 impact on cancer phenotypes. We characterized ELF4's mechanism of action via genomic and lipidomic analyses. A MAPK reporter assay verified ELF4's impact on MAPK signaling, and qRT-PCR and western blotting were used to corroborate ELF4 regulatory role on most relevant target genes.
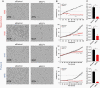
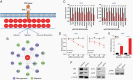
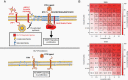
Results: ELF4 knockdown resulted in significant proliferation delay and apoptosis in GBM cells and long-term growth delay and morphological changes in glioma stem cells (GSCs). Transcriptomic analyses revealed that ELF4 controls two interlinked pathways: 1) Receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and 2) Lipid dynamics. ELF4 modulation directly affected receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling, as mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activity was dependent upon ELF4 levels. Furthermore, shotgun lipidomics revealed that ELF4 depletion disrupted several phospholipid classes, highlighting ELF4's importance in lipid homeostasis.
Conclusions: We found that ELF4 is critical for the GBM cell identity by controlling genes of two dependent pathways: RTK signaling (SRC, PTK2B, and TNK2) and lipid dynamics (LRP1, APOE, ABCA7, PLA2G6, and PITPNM2). Our data suggest that targeting these two pathways simultaneously may be therapeutically beneficial to GBM patients.
Keywords: ELF4; RTK signaling; glioblastoma; lipid dynamics; miRNA-transcription factor networks.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):987–996. - PubMed
-
- Weller M, Felsberg J, Hartmann C, et al. Molecular predictors of progression-free and overall survival in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma: a prospective translational study of the German Glioma Network. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(34):5743–5750. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

