Activity-dependent endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ uptake depends on Kv2.1-mediated endoplasmic reticulum/plasma membrane junctions to promote synaptic transmission
- PMID: 35862456
- PMCID: PMC9335237
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2117135119
Activity-dependent endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ uptake depends on Kv2.1-mediated endoplasmic reticulum/plasma membrane junctions to promote synaptic transmission
Abstract
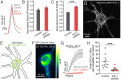
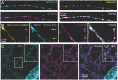
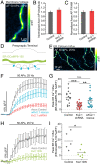
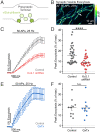
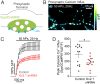
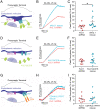
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) forms a continuous and dynamic network throughout a neuron, extending from dendrites to axon terminals, and axonal ER dysfunction is implicated in several neurological disorders. In addition, tight junctions between the ER and plasma membrane (PM) are formed by several molecules including Kv2 channels, but the cellular functions of many ER-PM junctions remain unknown. Recently, dynamic Ca2+ uptake into the ER during electrical activity was shown to play an essential role in synaptic transmission. Our experiments demonstrate that Kv2.1 channels are necessary for enabling ER Ca2+ uptake during electrical activity, as knockdown (KD) of Kv2.1 rendered both the somatic and axonal ER unable to accumulate Ca2+ during electrical stimulation. Moreover, our experiments demonstrate that the loss of Kv2.1 in the axon impairs synaptic vesicle fusion during stimulation via a mechanism unrelated to voltage. Thus, our data demonstrate that a nonconducting role of Kv2.1 exists through its binding to the ER protein VAMP-associated protein (VAP), which couples ER Ca2+ uptake with electrical activity. Our results further suggest that Kv2.1 has a critical function in neuronal cell biology for Ca2+ handling independent of voltage and reveals a critical pathway for maintaining ER lumen Ca2+ levels and efficient neurotransmitter release. Taken together, these findings reveal an essential nonclassical role for both Kv2.1 and the ER-PM junctions in synaptic transmission.
Keywords: Kv2; calcium; endoplasmic reticulum; exocytosis; synaptic transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuronal ER-plasma membrane junctions organized by Kv2-VAP pairing recruit Nir proteins and affect phosphoinositide homeostasis.J Biol Chem. 2019 Nov 22;294(47):17735-17757. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007635. Epub 2019 Oct 8. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31594866 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of VAPA and VAPB as Kv2 Channel-Interacting Proteins Defining Endoplasmic Reticulum-Plasma Membrane Junctions in Mammalian Brain Neurons.J Neurosci. 2018 Aug 29;38(35):7562-7584. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0893-18.2018. Epub 2018 Jul 16. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30012696 Free PMC article.
-
Kv2 channels create endoplasmic reticulum / plasma membrane junctions: a brief history of Kv2 channel subcellular localization.Channels (Austin). 2019 Dec;13(1):88-101. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2019.1568824. Channels (Austin). 2019. PMID: 30712450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kv2 potassium channels form endoplasmic reticulum/plasma membrane junctions via interaction with VAPA and VAPB.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jul 31;115(31):E7331-E7340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1805757115. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29941597 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium channel signalling at neuronal endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane junctions.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Aug 28;52(4):1617-1629. doi: 10.1042/BST20230819. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 38934485 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The complex web of membrane contact sites in brain aging and neurodegeneration.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Aug 8;82(1):301. doi: 10.1007/s00018-025-05830-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40779198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct cellular expression and subcellular localization of Kv2 voltage-gated K+ channel subtypes in dorsal root ganglion neurons conserved between mice and humans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 24:2023.03.01.530679. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.01.530679. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Comp Neurol. 2024 Feb;532(2):e25575. doi: 10.1002/cne.25575. PMID: 38187582 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Presynaptic endoplasmic reticulum architecture and hereditary spastic paraplegia.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Mar;19(3):485-486. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.380885. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37721265 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
NPC1-dependent alterations in KV2.1-CaV1.2 nanodomains drive neuronal death in models of Niemann-Pick Type C disease.Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 28;14(1):4553. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39937-w. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37507375 Free PMC article.
-
VAP spatially stabilizes dendritic mitochondria to locally support synaptic plasticity.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 4;15(1):205. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44233-8. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38177103 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

