Susceptibility to movement-evoked pain following resistance exercise
- PMID: 35862479
- PMCID: PMC9302845
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271336
Susceptibility to movement-evoked pain following resistance exercise
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the: (1) role of basic muscle pain sensitivity and psychological factors in the prediction of movement-evoked pain (MEP) following delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS), and (2) association of MEP with changes in systemic muscle pain sensitivity following DOMS induction.
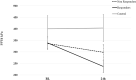
Methods: Fifty-one participants were assigned to either eccentric resistance exercise or control groups. They completed questionnaires evaluating psychological distress and underwent muscle pain sensitivity evaluation by the pressure pain threshold (PPT) test at the exercised and remote muscles, before and 24 hours following the intervention. MEP intensity was determined in response to lifting a 3kg canister using a visual analogue scale (VAS).
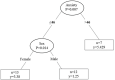
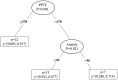
Results: The exercise group demonstrated MEP intensity of 5/10 on VAS and reduced PPTs at the main exercised muscle (p<0.001). A regression tree analyses revealed that the level of anxiety trait predicted a higher MEP intensity. A secondary analysis showed that 53% participants who were DOMS responders (MEP > mild intensity; ≥ 3/10 VAS) exhibited decreased PPTs in the exercised (p<0.001) and remote (p = 0.027) muscles following eccentric exercise. Characterization of DOMS responders revealed that, at baseline, they had lower PPTs in the exercised (p = 0.004) and remote (p = 0.001) muscles and reported higher psychological distress i.e., anxiety trait and depression symptoms (p<0.05), compared to non-responders. A regression analysis revealed that lower PPT or high levels of anxiety trait increased the probability to become a responder (p = 0.001).
Conclusions: Susceptibility to MEP following DOMS is determined by muscle pain hypersensitivity and high levels of anxiety trait. MEP at the early stage of DOMS is linked with an increase in systemic muscle pain sensitivity suggestive of central mechanisms. This knowledge is valuable in translating science into clinical musculoskeletal pain management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Armstrong RB. Mechanisms of exercise-induced delayed onset muscular soreness: a brief review. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1984;16(6):529–38. Epub 1984/12/01. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong RB. Initial events in exercise-induced muscular injury. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1990;22(4):429–35. Epub 1990/08/01. . - PubMed
-
- Vadasz B, Gohari J, West DW, Grosman-Rimon L, Wright E, Ozcakar L, et al. Improving characterization and diagnosis quality of myofascial pain syndrome: a systematic review of the clinical and biomarker overlap with delayed onset muscle soreness. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2020;56(4):469–78. Epub 2020/02/20. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.20.05820-7 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

