Performance of 22 Rapid Lateral Flow Tests for SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Detection and Influence of "Variants of Concern": Implications for Clinical Use
- PMID: 35862982
- PMCID: PMC9430704
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01157-22
Performance of 22 Rapid Lateral Flow Tests for SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Detection and Influence of "Variants of Concern": Implications for Clinical Use
Abstract
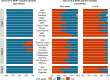
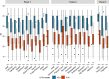
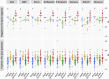
Large-scale head-to-head assessment of the performance of lateral-flow tests (LFTs) for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) antigen is required in the context of the continuous emergence of new viral variants. The aim of this study was to evaluate the performance of 22 rapid LFTs for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigens. The clinical performance of 22 LFTs was evaluated in 1,157 samples collected in the Greater Paris area. The 8 best-performing LFTs were further assessed for their ability to detect 4 variants of concern (VOC), including the alpha, beta, delta, and omicron (BA.1) variants. The specificity of SARS-CoV-2 LFTs was generally high (100% for 15 of them) but was insufficient (<75%) for 3 tests. Sensitivity of the LFTs varied from 30.0% to 79.7% compared to nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT). Using a cycle threshold (CT) cutoff of ≤25, sensitivity of the assays ranged from 59.7% to 100%. The 8 best-performing assays had a sensitivity of ≥80% for the detection of the 4 VOC when the CT was ≤25. Falsely negative SARS-CoV-2 antigen LFT results were observed with omicron, due to the occurrence of low viral loads (CT > 30 in 32% of samples) during the two first days following symptom onset. Several LFTs exhibited satisfactory sensitivity and specificity, whereas a few others yielded an unacceptable proportion of false-positive results and/or lacked sensitivity. The sensitivity of the best-performing assays was not influenced by VOC, including alpha, beta, delta, and omicron variants. The ability of LFTs to detect the omicron variant could be reduced during the first days following symptom onset due to lower viral loads than with other variants. IMPORTANCE The use of lateral-flow tests (LFTs) to detect SARS-CoV-2 has expanded worldwide. LFTs detect SARS-CoV-2 viral antigen and are less sensitive than nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT). Their performance must be evaluated independently of the manufacturers. Our study assessed the performance of 22 SARS-CoV-2 antigen LFTs in large panels of well-characterized samples. The majority of LFTs tested exhibited satisfactory sensitivity and specificity, while some assays yielded unacceptable proportions of false-positive results, and others lacked sensitivity for samples containing large amounts of virus. The sensitivity of the best-performing assays did not vary according to the VOC, including the alpha, beta, delta, and omicron variants.
Keywords: SARS CoV-2; lateral-flow tests; variants of concern.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare a conflict of interest. S.F. served as a speaker for Abbott diagnostics, GSK, MSD, and Cepheid. C.R. served as Advisor and speaker for illumina. S.C. served as Advisor and speaker for Cepheid, Gilead Sciences, Roche Diagnostics, Abbott Molecular. J.-M.P. served as Advisor and speaker for Gilead Sciences, Abbvie, Merck, Assembly Biosciences, Arbutus.
Figures

References
-
- Fourati S, Langendorf C, Audureau E, Challine D, Michel J, Soulier A, Ahnou N, Désveaux I, Picard O, Ortonne V, Gourgeon A, Mills C, Hémery F, Rieux C, Pawlotsky J-M, Malou N, Chevaliez S. 2021. Performance of six rapid diagnostic tests for SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection and implications for practical use. J Clin Virol 142:104930. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104930. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fourati S, Soulier A, Gourgeon A, Khouider S, Langlois C, Galbin A, Bouter AL, Rodriguez C, Joanny M, Dublineau A, Challine D, Bouvier-Alias M, Chevaliez S, Audureau É, Pawlotsky J-M. 2022. Performance of a high-throughput, automated enzyme immunoassay for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigen, including in viral “variants of concern”: implications for clinical use. J Clin Virol 146:105048. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2021.105048. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- European Commission Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety, Public health, Health Security. 2022. EU health preparedness: a common list of COVID-19 rapid antigen tests; A common standardised set of data to be included in COVID-19 test result certificates and A common list of COVID-19 laboratory based antigenic assays. https://health.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2022-06/covid-19_rat_common-lis....
-
- World Health Organization. Antigen-detection in the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. 2021. https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/antigen-detection-in-th.... Retrieved 10 November 2021.
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

