Spatiotemporal dynamics of EEG microstates in four- to eight-year-old children: Age- and sex-related effects
- PMID: 35863172
- PMCID: PMC9301511
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dcn.2022.101134
Spatiotemporal dynamics of EEG microstates in four- to eight-year-old children: Age- and sex-related effects
Abstract
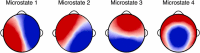
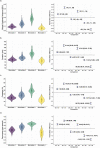
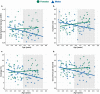
The ultrafast spatiotemporal dynamics of large-scale neural networks can be examined using resting-state electroencephalography (EEG) microstates, representing transient periods of synchronized neural activity that evolve dynamically over time. In adults, four canonical microstates have been shown to explain most topographic variance in resting-state EEG. Their temporal structures are age-, sex- and state-dependent, and are susceptible to pathological brain states. However, no studies have assessed the spatial and temporal properties of EEG microstates exclusively during early childhood, a critical period of rapid brain development. Here we sought to investigate EEG microstates recorded with high-density EEG in a large sample of 103, 4-8-year-old children. Using data-driven k-means cluster analysis, we show that the four canonical microstates reported in adult populations already exist in early childhood. Using multiple linear regressions, we demonstrate that the temporal dynamics of two microstates are associated with age and sex. Source localization suggests that attention- and cognitive control-related networks govern the topographies of the age- and sex-dependent microstates. These novel findings provide unique insights into functional brain development in children captured with EEG microstates.
Keywords: Age; Brain development; Children; EEG microstates; Resting-state networks; Sex differences.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Ben-Shachar, M.S. (2018). TBT: Reject and interpolate channels on a epoch by epoch basis (2.6.1) [Computer software]. 〈 10.5281/zenodo.1241518〉. - DOI
-
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995;57(1):289–300.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

