Environmentally responsive reproduction: neuroendocrine signalling and the evolution of eusociality
- PMID: 35863739
- PMCID: PMC9586883
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cois.2022.100951
Environmentally responsive reproduction: neuroendocrine signalling and the evolution of eusociality
Abstract
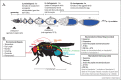
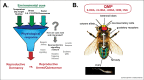
Eusociality is a rare but successful life-history strategy that is defined by the reproductive division of labour. In eusocial species, most females forgo their own reproduction to support that of a dominant female or queen. In many eusocial insects, worker reproduction is inhibited via dominance hierarchies or by pheromones produced by the queen and her brood. Here, we consider whether these cues may act as generic 'environmental signals', similar to temperature or nutrition stress, which induce a state of reproductive dormancy in some solitary insects. We review the recent findings regarding the mechanisms of reproductive dormancy in insects and highlight key gaps in our understanding of how environmental cues inhibit reproduction.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Danks H.V. Insect Dormancy: An Ecological Perspective. Biological Survey of Canada (Terrestrial Arthropods); 1987.
-
- Kostal V. Eco-physiological phases of insect diapause. J Insect Physiol. 2006;52:113–127. - PubMed
-
- Denlinger D.L. Regulation of diapause. Annu Rev Entomol. 2002;47:93–122. - PubMed
-
- Denlinger D.L. Cambridge University Press; 2022. Insect Diapause.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

