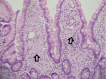
Whipple's disease unmasked by TNF inhibitor therapy for treatment of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 35863856
- PMCID: PMC9310182
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2022-250693
Whipple's disease unmasked by TNF inhibitor therapy for treatment of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
We report a patient with seronegative rheumatoid arthritis diagnosed with Whipple's disease following treatment of tumour necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFI) therapy. Whipple's disease should be considered in patients with seronegative rheumatoid arthritis and other unexplained multisystem illness. The TNFI therapy and immunosuppressive therapies can unmask latent Whipple's disease.
Keywords: Hepatitis and other GI infections; Infection (gastroenterology).
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2022. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Whipple's disease mimicking rheumatoid arthritis can cause misdiagnosis and treatment failure.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017 May 25;12(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s13023-017-0630-4. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017. PMID: 28545554 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors Exacerbate Whipple's Disease by Reprogramming Macrophage and Inducing Apoptosis.Front Immunol. 2021 May 20;12:667357. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.667357. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34093562 Free PMC article.
-
[Whipple's disease, a non-rheumatoid cause of seronegative arthritis].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2023 Mar 16;167:D6697. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2023. PMID: 36943167 Dutch.
-
Lyme disease and Whipple's disease: a comprehensive review for the rheumatologist.Adv Rheumatol. 2024 Mar 4;64(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s42358-024-00359-x. Adv Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38438928 Review.
-
[Palindromic rheumatism disclosing Whipple's disease. Study of 2 personal cases].Rev Rhum Ed Fr. 1994 Jan;61(1):44-8. Rev Rhum Ed Fr. 1994. PMID: 7528077 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Fever and Increased Gastrointestinal Uptake on Positron Emission Tomography after Anti-Tumour Necrosis Factor Therapy: A Case Report of Whipple's Disease.Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2024 Apr 20;18(1):221-230. doi: 10.1159/000538462. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38645407 Free PMC article.
-
Human genetics of Whipple's disease.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2025 Sep 1;37(5):316-320. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000001088. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40062480 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical