Urate crystal deposition is associated with inflammatory markers and carotid artery pathology in patients with intercritical gout: results from the NOR-Gout study
- PMID: 35863863
- PMCID: PMC9310249
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002348
Urate crystal deposition is associated with inflammatory markers and carotid artery pathology in patients with intercritical gout: results from the NOR-Gout study
Abstract
Background: Gout is of unknown reason associated with cardiovascular disease. Ultrasound is sensitive for detecting crystal deposition and plasma calprotectin is a sensitive inflammatory marker. This study explores the associations between crystal deposition, inflammation and carotid artery pathology.
Method: A cross-sectional analysis of baseline assessments from the NOR-Gout study was undertaken. Crystal deposition was assessed by ultrasound (double contour, tophi, aggregates) and dual-energy CT (DECT) and laboratory assessments included plasma calprotectin. The carotid arteries were bilaterally examined for carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) and presence of plaques. Spearman correlations, Mann-Whitney tests and linear regression analyses were used to explore associations between crystal deposition, inflammatory markers,and carotid pathology.
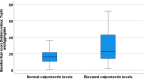
Results: 202 patients with intercritical gout (95.5% men, mean (SD) age 56.5 (13.8) years, disease duration 7.9 (7.7) years) were included. Calprotectin was correlated with all scores of crystal deposition by ultrasound (r=0.26-0.32, p<0.001) and DECT (r=0.15, p<0.05). cIMT was correlated with sum score aggregates (r=0.18-0.22, p<0.05). Patients with large tophi had higher levels of calprotectin as well as more frequent carotid plaque (p<0.05).
Conclusions: Study findings point towards crystal deposition contributing to subclinical inflammation with subsequent vascular implications. However, future longitudinal studies are needed to confirm such causal relationships.
Keywords: Cardiovascular Diseases; Gout; Inflammation; Ultrasonography.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Dr. Hammer reports personal fees from AbbVie, Lilly, UCB and Novartis, outside the submitted work. Dr. Rollefstad has no disclosures. Msc Jensen has no disclosures.Dr. Karoliussen has no disclosures.Dr. Terslev reports personal fees from Novartis, Roche, BMS and Pfizer outside the submitted work.Dr. Haavardsholm reports personal fees from Pfizer, UCB, Eli Lilly, Celgene, Janssen-Cilag, AbbVie and Gilead outside the submitted work.Dr. Kvien reports grants and personal fees from AbbVie, MSD, UCB, Hospira/Pfizer, Eli-Lilly, grants from BMS, personal fees from Roche, Hikma, Orion, Sanofi, Celltrion, Sandoz, Biogen, Amgen, Egis, Ewopharma and Mylan, outside the submitted work.Dr. Semb has received speaker honoraria and/or consulting fee from Novartis, AbbVie, Sanofi, KPMG, Bayer and Lilly and a collaborative agreement for independent research from Eli Lilly outside the submitted work.Dr. Uhlig reports personal fees from Galapagos, Grünenthal, Novartis, Pfizer, SOBI and UCB outside the submitted work.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical