Exploiting the sp2 character of bicyclo[1.1.1]pentyl radicals in the transition-metal-free multi-component difunctionalization of [1.1.1]propellane
- PMID: 35864151
- PMCID: PMC9420824
- DOI: 10.1038/s41557-022-00979-0
Exploiting the sp2 character of bicyclo[1.1.1]pentyl radicals in the transition-metal-free multi-component difunctionalization of [1.1.1]propellane
Abstract
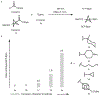
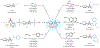
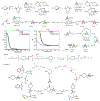
Strained bicyclic substructures are increasingly relevant in medicinal chemistry discovery research because of their role as bioisosteres. Over the last decade, the successful use of bicyclo[1.1.1]pentane (BCP) as a para-disubstituted benzene replacement has made it a highly valuable pharmacophore. However, various challenges, including limited and lengthy access to useful BCP building blocks, are hampering early discovery research. Here we report a single-step transition-metal-free multi-component approach to synthetically versatile BCP boronates. Radicals derived from commonly available carboxylic acids and organohalides perform additions onto [1.1.1]propellane to afford BCP radicals, which then engage in polarity-matched borylation. A wide array of alkyl-, aryl- and alkenyl-functionalized BCP boronates were easily prepared. Late-stage functionalization performed on natural products and approved drugs proceeded with good efficiency to generate the corresponding BCP conjugates. Various photoredox transformations forging C-C and C-N bonds were demonstrated by taking advantage of BCP trifluoroborate salts derived from the BCP boronates.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- van de Waterbeemd H & Gifford E ADMET in silico modelling: towards prediction paradise? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 2, 192–204 (2003). - PubMed
-
- M. Honorio K, L. Moda T & D. Andricopulo A Pharmacokinetic properties and in silico ADME modeling in drug discovery. Med. Chem 9, 163–176 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Lovering F, Bikker J & Humblet C Escape from flatland: increasing saturation as an approach to improving clinical success. J. Med. Chem 52, 6752–6756 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa M & Hashimoto Y Improvement in aqueous solubility in small molecule drug discovery programs by disruption of molecular planarity and symmetry. J. Med. Chem 54, 1539–1554 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Meanwell NA Synopsis of some recent tactical application of bioisosteres in drug design. J. Med. Chem 54, 2529–2591 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

