TRPM7 restrains plasmin activity and promotes transforming growth factor-β1 signaling in primary human lung fibroblasts
- PMID: 35864199
- PMCID: PMC9302958
- DOI: 10.1007/s00204-022-03342-x
TRPM7 restrains plasmin activity and promotes transforming growth factor-β1 signaling in primary human lung fibroblasts
Abstract
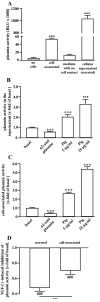
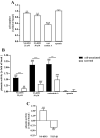
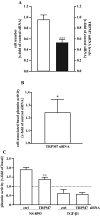
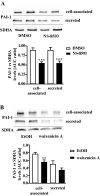
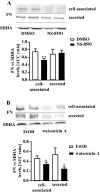
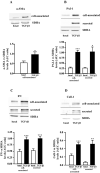
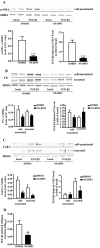
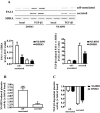
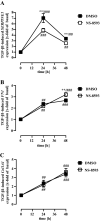
Sustained exposure of the lung to various environmental or occupational toxins may eventually lead to pulmonary fibrosis, a devastating disease with no cure. Pulmonary fibrosis is characterized by excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins such as fibronectin and collagens. The peptidase plasmin degrades the ECM, but protein levels of the plasmin activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) are increased in fibrotic lung tissue, thereby dampening plasmin activity. Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)-induced activation of SMAD transcription factors promotes ECM deposition by enhancing collagen, fibronectin and PAI-1 levels in pulmonary fibroblasts. Hence, counteracting TGF-β1-induced signaling is a promising approach for the therapy of pulmonary fibrosis. Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M Member 7 (TRPM7) supports TGF-β1-promoted SMAD signaling in T-lymphocytes and the progression of fibrosis in kidney and heart. Thus, we investigated possible effects of TRPM7 on plasmin activity, ECM levels and TGF-β1 signaling in primary human pulmonary fibroblasts (pHPF). We found that two structurally unrelated TRPM7 blockers enhanced plasmin activity and reduced fibronectin or PAI-1 protein levels in pHPF under basal conditions. Further, TRPM7 blockade strongly inhibited fibronectin and collagen deposition induced by sustained TGF-β1 stimulation. In line with these data, inhibition of TRPM7 activity diminished TGF-β1-triggered phosphorylation of SMAD-2, SMAD-3/4-dependent reporter activation and PAI-1 mRNA levels. Overall, we uncover TRPM7 as a novel supporter of TGF-β1 signaling in pHPF and propose TRPM7 blockers as new candidates to control excessive ECM levels under pathophysiological conditions conducive to pulmonary fibrosis.
Keywords: Plasmin; Primary human lung fibroblasts; Pulmonary fibrosis; TGF-β1; TRPM7.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TGF-β1-elevated TRPM7 channel regulates collagen expression in hepatic stellate cells via TGF-β1/Smad pathway.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Oct 15;280(2):335-44. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Aug 19. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25150141
-
p90RSK Inhibition Ameliorates TGF-β1 Signaling and Pulmonary Fibrosis by Inhibiting Smad3 Transcriptional Activity.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2020 Feb 22;54(2):195-210. doi: 10.33594/000000214. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32083406
-
Plasminogen activation induced pericellular fibronectin proteolysis promotes fibroblast apoptosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008 Jan;38(1):78-87. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0174OC. Epub 2007 Jul 26. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 17656680 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of non-SMAD and SMAD signaling in TGF-beta1-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 gene expression in vascular smooth muscle cells.Thromb Haemost. 2008 Dec;100(6):976-83. Thromb Haemost. 2008. PMID: 19132220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGF-β1-p53 cooperativity regulates a profibrotic genomic program in the kidney: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications.FASEB J. 2019 Oct;33(10):10596-10606. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900943R. Epub 2019 Jul 6. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31284746 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A dual role for ERK-1/2 in the regulation of plasmin activity and cell migration in metastatic NSCLC-H1299 cells.Arch Toxicol. 2023 Dec;97(12):3113-3128. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03600-6. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Arch Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37712947 Free PMC article.
-
GTSE1-driven ZEB1 stabilization promotes pulmonary fibrosis through the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.Mol Ther. 2024 Nov 6;32(11):4138-4157. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.09.029. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 39342428 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in therapeutic use of transforming growth factor-beta inhibitors in cancer and fibrosis.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 25;15:1489701. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1489701. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40352593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Baricitinib improves pulmonary fibrosis in mice with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease by inhibiting the Jak2/Stat3 signaling pathway.Adv Rheumatol. 2023 Aug 28;63(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s42358-023-00325-z. Adv Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37641106
-
Inactivation of TRPM7 Kinase Targets AKT Signaling and Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression in Human CML Cells.Function (Oxf). 2023 Sep 15;4(6):zqad053. doi: 10.1093/function/zqad053. eCollection 2023. Function (Oxf). 2023. PMID: 37786778 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

