Comparative effectiveness and safety of glargine 300 U/mL versus degludec 100 U/mL in insulin-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes. A multicenter retrospective real-world study (RESTORE-2 NAIVE STUDY)
- PMID: 35864262
- PMCID: PMC9402723
- DOI: 10.1007/s00592-022-01925-9
Comparative effectiveness and safety of glargine 300 U/mL versus degludec 100 U/mL in insulin-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes. A multicenter retrospective real-world study (RESTORE-2 NAIVE STUDY)
Abstract
Aims: This study assessed comparative effectiveness of glargine 300 U/mL (Gla-300) versus degludec 100 U/mL (Deg-100) in insulin-naïve patients with T2D.
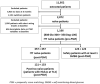
Methods: This is a retrospective, multicenter, non-inferiority study based on electronic medical records. All patients initiating Gla-300 or Deg-100 were 1:1 propensity score-matched (PSM). Linear mixed models were used to assess the changes in continuous endpoints. Incidence rates (IR) of hypoglycemia were compared using Poisson's regression models.
Results: Nineteen centers provided data on 357 patients in each PSM cohort. HbA1c after 6 months (primary endpoint) decreased by - 1.70% (95%CI - 1.90; - 1.50) in Gla-300 group and - 169% (95%CI - 1.89; - 1.49) in Deg-100 group, confirming non-inferiority of Gla-300 versus Deg-100. Fasting blood glucose (BG) decreased by ~60 mg/dl in both groups; body weight remained unchanged. In both groups, the mean starting dose was 12U (0.15U/kg) and it was slightly titrated to 16U (0.20U/kg). IR (episodes per patient-months) of BG ≤70 mg/dl was 0.13 in Gla-300 group and 0.14 in Deg-100 group (p=0.87). IR of BG <54 mg/dL was 0.02 in both groups (p=0.49). No severe hypoglycemia occurred.
Conclusion: Initiating Gla-300 or Deg-100 was associated with similar improvements in glycemic control, no weight gain and low hypoglycemia rates, without severe episodes during 6 months of treatment.
Keywords: Basal insulin; Degludec 100; Effectiveness; Glargine 300; Naïve; Safety; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
GPF has received consultancy of lecture fees from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer, Lilly, MSC, NovoNordisk, Mundipharma, Sanofi, Servier and Takeda. RB has received consultancy of lecture fees from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Lilly, NovoNordisk, Mundipharma and Sanofi. ML is an employee of Sanofi and may hold shares and/or stock options in the company. MCR and AN have received funding for research from Sanofi, NovoNordisk, Alfasigma, Artsana, AstraZeneca, Johnson&Johnson, Medtronic, Shionogi, SOBI, Meteda and Theras. DC has received consultation fees and speaker honoraria from Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Roche Diagnostics, Sanofi and Takeda.
Figures
References
-
- Buse JB, Wexler DJ, Tsapas A, et al. update to: Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Diabetologia. 2020;63:221–228. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-05039-w. - DOI - PubMed
-
- AMD/SID. Standard italiani per la cura del diabete mellito 2018. https://www.siditalia.it/pdf/Standard%20di%20Cura%20AMD%20-%20SID%202018... [last access 29 June 2021]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous