Dynamic enhancer transcription associates with reprogramming of immune genes during pattern triggered immunity in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 35864475
- PMCID: PMC9301868
- DOI: 10.1186/s12915-022-01362-8
Dynamic enhancer transcription associates with reprogramming of immune genes during pattern triggered immunity in Arabidopsis
Abstract
Background: Enhancers are cis-regulatory elements present in eukaryote genomes, which constitute indispensable determinants of gene regulation by governing the spatiotemporal and quantitative expression dynamics of target genes, and are involved in multiple life processes, for instance during development and disease states. The importance of enhancer activity has additionally been highlighted for immune responses in animals and plants; however, the dynamics of enhancer activities and molecular functions in plant innate immunity are largely unknown. Here, we investigated the involvement of distal enhancers in early innate immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana.
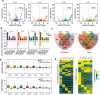
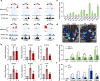
Results: A group of putative distal enhancers producing low-abundance transcripts either unidirectionally or bidirectionally are identified. We show that enhancer transcripts are dynamically modulated in plant immunity triggered by microbe-associated molecular patterns and are strongly correlated with open chromatin, low levels of methylated DNA, and increases in RNA polymerase II targeting and acetylated histone marks. Dynamic enhancer transcription is correlated with target early immune gene expression patterns. Cis motifs that are bound by immune-related transcription factors, such as WRKYs and SARD1, are highly enriched within upregulated enhancers. Moreover, a subset of core pattern-induced enhancers are upregulated by multiple patterns from diverse pathogens. The expression dynamics of putative immunity-related enhancers and the importance of WRKY binding motifs for enhancer function were also validated.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates the general occurrence of enhancer transcription in plants and provides novel information on the distal regulatory landscape during early plant innate immunity, providing new insights into immune gene regulation and ultimately improving the mechanistic understanding of the plant immune system.
Keywords: Cis-regulatory elements; Enhancer RNAs; Enhancers; Plant innate immunity; Transcriptional regulation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
An enhancer-promoter-transcription factor module orchestrates plant immune homeostasis by constraining camalexin biosynthesis.Mol Plant. 2025 Jan 6;18(1):95-113. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2024.12.002. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Mol Plant. 2025. PMID: 39628054
-
Novel mRNAs 3' end-associated cis-regulatory elements with epigenomic signatures of mammalian enhancers in the Arabidopsis genome.RNA. 2019 Oct;25(10):1242-1258. doi: 10.1261/rna.071209.119. Epub 2019 Jul 16. RNA. 2019. PMID: 31311821 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenomic analysis reveals a dynamic and context-specific macrophage enhancer landscape associated with innate immune activation and tolerance.Genome Biol. 2022 Jun 24;23(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s13059-022-02702-1. Genome Biol. 2022. PMID: 35751107 Free PMC article.
-
Towards genome-wide prediction and characterization of enhancers in plants.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017 Jan;1860(1):131-139. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.06.006. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017. PMID: 27321818 Review.
-
Enhancer RNAs: a missing regulatory layer in gene transcription.Sci China Life Sci. 2019 Jul;62(7):905-912. doi: 10.1007/s11427-017-9370-9. Epub 2018 Dec 26. Sci China Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30593613 Review.
Cited by
-
Differences in transcription initiation directionality underlie distinctions between plants and animals in chromatin modification patterns at genes and cis-regulatory elements.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 5:2023.11.03.565513. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.03.565513. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: G3 (Bethesda). 2024 Mar 6;14(3):jkae016. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkae016. PMID: 37961418 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Enhancers in Plant Development, Adaptation and Evolution.Plant Cell Physiol. 2025 May 17;66(4):461-476. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcae121. Plant Cell Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39412125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences in transcription initiation directionality underlie distinctions between plants and animals in chromatin modification patterns at genes and cis-regulatory elements.G3 (Bethesda). 2024 Mar 6;14(3):jkae016. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkae016. G3 (Bethesda). 2024. PMID: 38253712 Free PMC article.
-
A fine-scale Arabidopsis chromatin landscape reveals chromatin conformation-associated transcriptional dynamics.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 16;15(1):3253. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47678-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38627396 Free PMC article.
-
The coordinated responses of host plants to diverse N-acyl homoserine lactones.Plant Signal Behav. 2024 Dec 31;19(1):2356406. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2024.2356406. Epub 2024 May 24. Plant Signal Behav. 2024. PMID: 38785260 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

