Engineered exosome-mediated delivery of circDIDO1 inhibits gastric cancer progression via regulation of MiR-1307-3p/SOCS2 Axis
- PMID: 35864511
- PMCID: PMC9306104
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-022-03527-z
Engineered exosome-mediated delivery of circDIDO1 inhibits gastric cancer progression via regulation of MiR-1307-3p/SOCS2 Axis
Abstract
Background: Our previous study has identified a novel circRNA (circDIDO1) that is down-regulated in gastric cancer (GC) and significantly inhibits GC progression. The purpose of this study is to identify the molecular mechanism for circDIDO1 and to evaluate the therapeutic effect of circDIDO1 in GC.
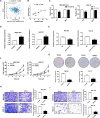
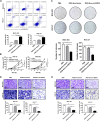
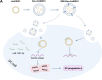
Methods: By combining bioinformatic analysis with RNA sequencing data, we predicted the potential target of circDIDO1 and further validated the regulatory mechanisms for its tumor suppressor function in GC. RIP assay, luciferase reporter assay and in vitro cell function assays were performed to analyze circDIDO1-regulated downstream target genes. For the therapeutic study, circDIDO1-loaded, RGD-modified exosomes (RGD-Exo-circDIDO1) were constructed and its anti-tumor efficacy and biological safety were evaluated in vitro and in vivo.
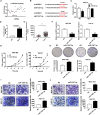
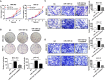
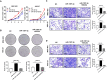
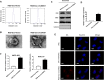
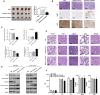
Results: CircDIDO1 inhibited GC progression by regulating the expression of the signal transducer inhibitor SOSC2 through sponging miR-1307-3p. Overexpression of circDIDO1 or SOSC2 antagonized the oncogenic role of miR-1307-3p. RGD-Exo-circDIDO1 could efficiently deliver circDIDO1 to increase SOCS2 expression in GC cells. Compared with PBS and RGD-Exo-vector treatment, RGD-Exo-circDIDO1 treatment significantly inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion of GC cells while promoted cell apoptosis. The therapeutic efficacy of RGD-Exo-circDIDO1 was further confirmed in a mouse xenograft tumor model. In addition, major tissues including the heart, liver, spleen, lungs and kidneys showed no obvious histopathological abnormalities or lesions in the RGD-Exo-circDIDO1 treated group.
Conclusion: Our findings revealed that circDIDO1 suppressed the progression of GC via modulating the miR-1307-3p/SOSC2 axis. Systemic administration of RGD modified, circDIDO1 loaded exosomes repressed the tumorigenicity and aggressiveness of GC both in vitro and in vivo, suggesting that RGD-Exo-circDIDO1 could be used as a feasible nanomedicine for GC therapy.
Keywords: Cancer therapy; CirDIDO1; Exosomes; Gastric cancer; MiR-1307-3p; SOCS2.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author reports no competing interests in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CircDIDO1 inhibits gastric cancer progression by encoding a novel DIDO1-529aa protein and regulating PRDX2 protein stability.Mol Cancer. 2021 Aug 12;20(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01390-y. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34384442 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal transfer of miR-15b-3p enhances tumorigenesis and malignant transformation through the DYNLT1/Caspase-3/Caspase-9 signaling pathway in gastric cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Feb 10;39(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1511-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32039741 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-originated exosomal circDIDO1 suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation by miR-141-3p/PTEN/AKT pathway in human liver fibrosis.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):440-453. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2030428. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35099348 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric cancer-derived exosomal miR-519a-3p promotes liver metastasis by inducing intrahepatic M2-like macrophage-mediated angiogenesis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Oct 10;41(1):296. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02499-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36217165 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA CircCACTIN Promotes Gastric Cancer Progression by Sponging MiR-331-3p and Regulating TGFBR1 Expression.Int J Biol Sci. 2019 Apr 22;15(5):1091-1103. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.31533. eCollection 2019. Int J Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31182928 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Regulatory mechanism and promising clinical application of exosomal circular RNA in gastric cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Nov 29;13:1236679. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1236679. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38094607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles in cancer: golden goose or Trojan horse.J Mol Cell Biol. 2024 Oct 21;16(5):mjae025. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjae025. J Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38796692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for gastric cancer: A comprehensive update from emerging functions to clinical significances.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 28;13:1037120. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1037120. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36386850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered Extracellular Vesicles: Emerging Therapeutic Strategies for Translational Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 15;24(20):15206. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015206. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal circRNA: emerging insights into cancer progression and clinical application potential.J Hematol Oncol. 2023 Jun 26;16(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01452-2. J Hematol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37365670 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

