Improvement of several stress response and sleep quality hormones in men and women after sleeping in a bed that protects against electromagnetic fields
- PMID: 35864547
- PMCID: PMC9306162
- DOI: 10.1186/s12940-022-00882-8
Improvement of several stress response and sleep quality hormones in men and women after sleeping in a bed that protects against electromagnetic fields
Abstract
Background: The electromagnetic fields (EMFs) emitted by the technologies affect the homeostatic systems (nervous, endocrine, and immune systems) and consequently the health. In a previous work, we observed that men and women, after 2 months of using a bed with a registered HOGO system, that prevents and drain EMFs, improved their immunity, redox and inflammatory states and rejuvenated their rate of aging or biological age. Since, EMFs can act as a chronic stressor stimulus, and affect the sleep quality. The objective of this work was to study in men and women (23-73 years old) the effect of sleeping for 2 months on that bed in the blood concentrations of several hormones related to stress response and sleep quality as well as to corroborate the rejuvenation of their biological age.
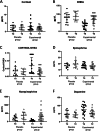
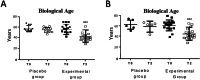
Methods: In 18 men and women, plasma concentration of cortisol, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine and dopamine), serotonin, oxytocin and melatonin were analyzed before and after 2 months of using the HOGO beds. A group of 10 people was used as placebo control. In another cohort of 25 men (20 experimental and 5 placebo), the effects of rest on the HOGO system on the concentration of cortisol and testosterone in plasma were studied. In all these volunteers, the biological age was analyzed using the Immunity Clock model.
Results: There is a significant increase in plasma concentration of DHEA, norepinephrine, serotonin, oxytocin, and melatonin as well as in testosterone, after resting for 2 months in that bed with the EMFs avoiding system. In addition, decreases in Cortisol/DHEA and Testosterone/cortisol ratio and plasma dopamine concentration were observed. No differences were found in placebo groups. In all participants that slept on HOGO beds, the biological age was reduced.
Conclusions: Sleeping in a bed that isolates from EMFs and drain them can be a possible strategy to improve the secretion of hormones related to a better response to stress and sleep quality, which means a better endocrine system, and consequently better homeostasis and maintenance of health. This fact was confirmed with the slowdown in the rate of aging checked with a rejuvenation of the biological age.
Keywords: Biological age; Electromagnetic fields; Hormones; Men and women; Sleep; Stress response.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The use of a bed with an insulating system of electromagnetic fields improves immune function, redox and inflammatory states, and decrease the rate of aging.Environ Health. 2020 Nov 23;19(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s12940-020-00674-y. Environ Health. 2020. PMID: 33228714 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of six months treatment with a 100 mg daily dose of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) on circulating sex steroids, body composition and muscle strength in age-advanced men and women.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1998 Oct;49(4):421-32. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2265.1998.00507.x. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1998. PMID: 9876338 Clinical Trial.
-
Bidirectional effect of electromagnetic fields on ketanserin-induced yawning in patients with multiple sclerosis: the role of melatonin.Int J Neurosci. 1996 Mar;85(1-2):93-9. doi: 10.3109/00207459608986354. Int J Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8727685
-
Resolution of sleep paralysis by weak electromagnetic fields in a patient with multiple sclerosis.Int J Neurosci. 1997 Aug;90(3-4):145-57. doi: 10.3109/00207459709000634. Int J Neurosci. 1997. PMID: 9352423 Review.
-
Microwave frequency electromagnetic fields (EMFs) produce widespread neuropsychiatric effects including depression.J Chem Neuroanat. 2016 Sep;75(Pt B):43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2015.08.001. Epub 2015 Aug 21. J Chem Neuroanat. 2016. PMID: 26300312 Review.
Cited by
-
Subjective Sleep Quality Versus Objective Accelerometric Measures of Sleep and Systemic Concentrations of Sleep-Related Hormones as Objective Biomarkers in Fibromyalgia Patients.Biomedicines. 2023 Jul 13;11(7):1980. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11071980. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37509619 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kafaee Razavi M, Raji RA, Maleki M, Dehghani H, Haghpeima A. Histopathological and immunohistochemical study of rat brain tissue after exposure to mobile phone radiation. Comp Clin Path. 2015;24:1271–1276. doi: 10.1007/s00580-015-2113-0. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

