MARCKSL1-2 reverses docetaxel-resistance of lung adenocarcinoma cells by recruiting SUZ12 to suppress HDAC1 and elevate miR-200b
- PMID: 35864549
- PMCID: PMC9306054
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-022-01605-w
MARCKSL1-2 reverses docetaxel-resistance of lung adenocarcinoma cells by recruiting SUZ12 to suppress HDAC1 and elevate miR-200b
Abstract
Background: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are implicated in the development of multiple cancers. In our previous study, we demonstrated that HDAC1/4-mediated silencing of microRNA-200b (miR-200b) enhances docetaxel (DTX)-resistance of human lung adenocarcinoma (LAD) cells.
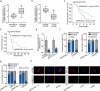
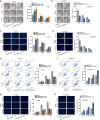
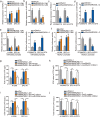
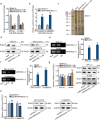
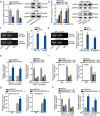
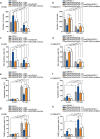
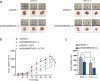
Methods and results: Herein, we probed the function of LncRNA MARCKSL1-2 (MARCKSL1-transcript variant 2, NR_052852.1) in DTX resistance of LAD cells. It was found that MARCKSL1-2 expression was markedly reduced in DTX-resistant LAD cells. Through gain- or loss- of function assays, colony formation assay, EdU assay, TUNEL assay, and flow cytometry analysis, we found that MARCKSL1-2 suppressed the growth and DTX resistance of both parental and DTX-resistant LAD cells. Moreover, we found that MARCKSL1-2 functioned in LAD through increasing miR-200b expression and repressing HDAC1. Mechanistically, MARCKSL1-2 recruited the suppressor of zeste 12 (SUZ12) to the promoter of histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) to strengthen histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) of HDAC1 promoter, thereby reducing HDAC1 expression. MARCKSL1-2 up-regulated miR-200b by blocking the suppressive effect of HDAC1 on the histone acetylation modification at miR-200b promoter. Furthermore, in vivo analysis using mouse xenograft tumor model supported that overexpression of MARCKSL1-2 attenuated the DTX resistance in LAD tumors.
Conclusions: We confirmed that MARCKSL1-2 alleviated DTX resistance in LAD cells by abolishing the inhibitory effect of HDAC1 on miR-200b via the recruitment of SUZ12. MARCKSL1-2 could be a promising target to improve the chemotherapy of LAD.
Keywords: Docetaxel-resistance; HDAC1; Lung adenocarcinoma; MARCKSL1–2; SUZ12; miR-200b.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histone deacetylase 1/Sp1/microRNA-200b signaling accounts for maintenance of cancer stem-like cells in human lung adenocarcinoma.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 3;9(10):e109578. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109578. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25279705 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC 1/4-mediated silencing of microRNA-200b promotes chemoresistance in human lung adenocarcinoma cells.Oncotarget. 2014 May 30;5(10):3333-49. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1948. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24830600 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-200b regulates autophagy associated with chemoresistance in human lung adenocarcinoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 20;6(32):32805-20. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5352. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26416454 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-200b reverses chemoresistance of docetaxel-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting E2F3.Cancer. 2012 Jul 1;118(13):3365-76. doi: 10.1002/cncr.26560. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22139708
-
Long noncoding RNA ROR regulates chemoresistance in docetaxel-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cells via epithelial mesenchymal transition pathway.Oncotarget. 2017 May 16;8(20):33144-33158. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16562. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28388536 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
WTAP-dependent N6-methyladenosine methylation of lncRNA TEX41 promotes renal cell carcinoma progression.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 21;14(1):24742. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76326-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39433619 Free PMC article.
-
Composition of Conditioned Media from Radioresistant and Chemoresistant Cancer Cells Reveals miRNA and Other Secretory Factors Implicated in the Development of Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 19;24(22):16498. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216498. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ctDNA-based postoperative molecular residual disease status in different subtypes of early-stage breast cancer.Gland Surg. 2022 Dec;11(12):1924-1935. doi: 10.21037/gs-22-634. Gland Surg. 2022. PMID: 36654951 Free PMC article.
-
KDELR3 is transcriptionally activated by FOXM1 and accelerates lung adenocarcinoma growth and metastasis via inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell apoptosis.Hum Cell. 2025 May 24;38(4):106. doi: 10.1007/s13577-025-01238-3. Hum Cell. 2025. PMID: 40411680
-
USP5-dependent HDAC1 promotes cisplatin resistance and the malignant progression of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating RILP acetylation levels.Thorac Cancer. 2025 Jan;16(1):e15478. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15478. Epub 2024 Nov 24. Thorac Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39582290 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

