MARCKSL1-2 reverses docetaxel-resistance of lung adenocarcinoma cells by recruiting SUZ12 to suppress HDAC1 and elevate miR-200b
- PMID: 35864549
- PMCID: PMC9306054
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-022-01605-w
MARCKSL1-2 reverses docetaxel-resistance of lung adenocarcinoma cells by recruiting SUZ12 to suppress HDAC1 and elevate miR-200b
Abstract
Background: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are implicated in the development of multiple cancers. In our previous study, we demonstrated that HDAC1/4-mediated silencing of microRNA-200b (miR-200b) enhances docetaxel (DTX)-resistance of human lung adenocarcinoma (LAD) cells.
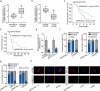
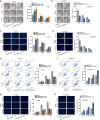
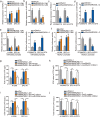
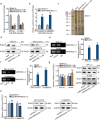
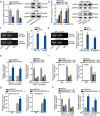
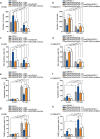
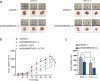
Methods and results: Herein, we probed the function of LncRNA MARCKSL1-2 (MARCKSL1-transcript variant 2, NR_052852.1) in DTX resistance of LAD cells. It was found that MARCKSL1-2 expression was markedly reduced in DTX-resistant LAD cells. Through gain- or loss- of function assays, colony formation assay, EdU assay, TUNEL assay, and flow cytometry analysis, we found that MARCKSL1-2 suppressed the growth and DTX resistance of both parental and DTX-resistant LAD cells. Moreover, we found that MARCKSL1-2 functioned in LAD through increasing miR-200b expression and repressing HDAC1. Mechanistically, MARCKSL1-2 recruited the suppressor of zeste 12 (SUZ12) to the promoter of histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) to strengthen histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) of HDAC1 promoter, thereby reducing HDAC1 expression. MARCKSL1-2 up-regulated miR-200b by blocking the suppressive effect of HDAC1 on the histone acetylation modification at miR-200b promoter. Furthermore, in vivo analysis using mouse xenograft tumor model supported that overexpression of MARCKSL1-2 attenuated the DTX resistance in LAD tumors.
Conclusions: We confirmed that MARCKSL1-2 alleviated DTX resistance in LAD cells by abolishing the inhibitory effect of HDAC1 on miR-200b via the recruitment of SUZ12. MARCKSL1-2 could be a promising target to improve the chemotherapy of LAD.
Keywords: Docetaxel-resistance; HDAC1; Lung adenocarcinoma; MARCKSL1–2; SUZ12; miR-200b.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

