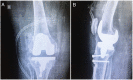
EXTENSOR MECHANISM TRANSPLANTATION AFTER KNEE PROSTHESIS: 70-MONTH FOLLOW-UP
- PMID: 35864839
- PMCID: PMC9270048
- DOI: 10.1590/1413-785220223001e253424
EXTENSOR MECHANISM TRANSPLANTATION AFTER KNEE PROSTHESIS: 70-MONTH FOLLOW-UP
Abstract
Objective: This article reports the range of motion, failure rate, and complications of patients with extensor mechanism injury after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) treated with extensor mechanism allograft with mid-term follow-up.
Methods: Patients undergoing post-ATJ extensor mechanism transplantation from 2009 to 2018 were retrospectively evaluated. Demographics, the reason for transplantation, elapsed time from arthroplasty to transplantation, related surgical factors, immobilization time, range of motion, transplant failure, and complications were collected. The minimum follow-up was 24 months.
Results: Twenty patients were evaluated. The mean follow-up was 70.8 +/- 33.6 months. The most common cause of extensor mechanism rupture was traumatic in 10 (50%) cases. Six patients underwent associated surgeries, one case of medial ligament complex reconstruction, and 5 cases of TKA revision. Eleven patients (55%) had transplant-related complications. The most common complication was an infection. Five cases presented transplant failure.
Conclusion: Patients who underwent extensor mechanism allograft transplantation after total knee arthroplasty had a 25% failure rate with a mean follow-up of 6 years. Although there was no loss of flexion with the procedure and prolonged immobilization, the complication rate was not low. Level of evidence IV; case series .
Objetivo: O objetivo do estudo foi relatar amplitude de movimento, taxa de falha e complicações de pacientes com lesão do mecanismo extensor após artroplastia total do joelho (ATJ) tratados com aloenxerto do mecanismo extensor com acompanhamento no médio prazo.
Métodos: Pacientes submetidos a transplante de mecanismo extensor pós-ATJ de 2009 a 2018 foram avaliados retrospectivamente. Foram avaliados dados demográficos, motivo do transplante, tempo decorrido da artroplastia ao transplante, fatores cirúrgicos relacionados, tempo de imobilização, arco de movimento, falha do transplante e complicações. O acompanhamento mínimo foi de 24 meses.
Resultados: Vinte pacientes foram avaliados. O tempo médio de acompanhamento foi de 70,8 +/- 33,6 meses. A causa mais comum de ruptura do mecanismo extensor foi traumática em 10 (50%) casos. Seis pacientes foram submetidos a cirurgias associadas, um caso de reconstrução do complexo ligamentar medial e 5 casos de revisão de ATJ. Onze pacientes (55%) tiveram complicações relacionadas ao transplante. A complicação mais comum foi a infecção. Cinco casos apresentaram falha do transplante.
Conclusão: Pacientes submetidos a transplante de aloenxerto de mecanismo extensor após artroplastia total de joelho apresentam taxa de falha de 25% com seguimento médio de 6 anos. Embora não tenha havido perda de flexão com o procedimento e com a imobilização prolongada, o índice de complicações não foi baixo. Nível de evidênvia IV; série de casos .
Keywords: Knee Arthroplasty; Knee Replacement Arthroplasties; Partial Knee Replacement.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no potential conflict of interest related to this article.
Figures
References
-
- Bovonratwet P., et al. Reasons and Risk Factors for 30-Day Readmission After Outpatient Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Review of 3015 Cases. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(9):2451–2457. - PubMed
-
- Lan RH Y.J., Samuel LT, Pappas MA, Brooks PJ, Kamath AF. How are We Measuring Cost-Effectiveness in Total Joint Arthroplasty Studies? Systematic Review of the Literature. The Journal of Arthroplasty. 2020 - PubMed
-
- Kurtz S., et al. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(4):780–785. - PubMed
-
- Maffulli N., et al. The Management of Extensor Mechanism Disruption After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2017;25(1):41–50. - PubMed
-
- Vajapey S.P., et al. Treatment of Extensor Tendon Disruption After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(6):1279–1286. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources