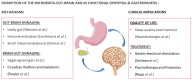
Editorial: Disruption of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Functional Dyspepsia and Gastroparesis: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications
- PMID: 35864983
- PMCID: PMC9295387
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.941810
Editorial: Disruption of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Functional Dyspepsia and Gastroparesis: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications
Keywords: disorders of gut-brain interaction (DGBI); functional dyspepsia (FD); functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGID); gastrointestinal (GI); microbiota-gut-brain axis (MGBA); small bowel bacterial overgrowth (SIBO).
Conflict of interest statement
NT reports, personal fees from, Allakos (gastric eosinophilic disease) (2021), Bayer [IBS] (2020), Planet Innovation (Gas capsule IBS) (2020), Takeda, Japan (gastroparesis) (2019), Viscera Labs, (USA 2021) (IBS-diarrhoea), Dr Falk Pharma (2020) (EoE), Glutagen (2020) (Celiac disease), IsoThrive (2021) (oesophageal microbiome), BluMaiden (2021), Rose Pharma (2021), Intrinsic Medicine (2021), Comvita Mānuka Honey (2021), Reckitt (2022) outside the submitted work. NT has a patent Nepean Dyspepsia Index (NDI) 1998, Biomarkers of IBS licensed, a patent Licensing Questionnaires Talley Bowel Disease Questionnaire licensed to Mayo/Talley, a patent Nestec European Patent licensed, and a patent Singapore Provisional Patent “Microbiota Modulation Of BDNF Tissue Repair Pathway” issued, “Diagnostic marker for functional gastrointestinal disorders” AustraWautersan Provisional Patent Application 2021901692. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment on
- The Editorial on the Research Topic Disruption of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Functional Dyspepsia and Gastroparesis: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources