Analysis of Ultrasonographic Characteristics of Early Hepatic Alveolar Echinococcosis
- PMID: 35865038
- PMCID: PMC9294286
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.918138
Analysis of Ultrasonographic Characteristics of Early Hepatic Alveolar Echinococcosis
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to investigate the ultrasonographic characteristics of early hepatic alveolar echinococcosis (HAE) and improve the qualitative diagnostic ability of sonographers.
Methods: The data of 80 positive cases of HAE screened and diagnosed by ultrasonography and serum immunology (33 males and 44 females with a mean age of 44.12 ± 14.31 y) were used in the study. The imaging characteristics of the lesions (i.e., intrahepatic distribution, shape, size, echo, blood flow, and growth characteristics) were analyzed retrospectively, and the ultrasonographic characteristics of early lesions were discussed in combination with their basic pathological changes.
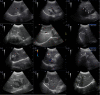
Results: Patients with lesions of the proliferative infiltration type accounted for 57.5% (46/80), the fibrous calcification type accounted for 26.25% (21/80), the necrotic liquefaction type accounted for 6.25% (5/80), and the mixed type accounted for 10% (8/80). Patients with lesions involving the right lobe and the left lobe accounted for 76.25% (61/80) and 11.25% (9/80), respectively, and with lesions involving both the left and right lobes accounted for 12.5% (10/80). There were statistically significant differences in diameter between all types of lesions (n = 88; F = 5.926 and P = 0.004). Focal hyperechoic and diffuse heterogenous nodular changes were the main manifestations of early proliferative infiltration lesions.
Conclusion: Ultrasonography is extremely valuable in the diagnosis of early HAE. Capillary hemangioma-like changes and hailstorm sign are the main characteristics of early lesions of HAE, and calcification is a common concomitant sign.
Keywords: alveolar echinococcosis; characteristics; concomitant sign; liver; ultrasonogram.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Liu, Sun, Wu, Xie and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ultrasonographic findings of small lesion of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis.Acta Trop. 2017 Oct;174:165-170. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2016.01.030. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Acta Trop. 2017. PMID: 26892870
-
Long-term follow-up of liver alveolar echinococcosis using echinococcosis multilocularis ultrasound classification.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Oct 28;27(40):6939-6950. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i40.6939. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34790016 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) and pathological images of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis (HAE) lesions.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016 May;20(10):1954-60. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27249592
-
An Overview of Hepatic Echinococcosis and the Characteristic CT and MRI Imaging Manifestations.Infect Drug Resist. 2021 Oct 27;14:4447-4455. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S331957. eCollection 2021. Infect Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 34737585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver transplantation for hepatic alveolar echinococcosis: literature review and three new cases.Infect Dis (Lond). 2018 Jun;50(6):452-459. doi: 10.1080/23744235.2018.1428823. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Infect Dis (Lond). 2018. PMID: 29363377 Review.
References
-
- Matsumoto J, Kouguchi H, Oku Y, Yagi K. Primary alveolar echinococcosis: course of larval development and antibody responses in intermediate host rodents with different genetic backgrounds after oral infection with eggs of Echinococcus multilocularis. Parasitol Int. (2010) 59(3):435–44. 10.1016/j.parint.2010.06.003 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

