Ionic liquid-immobilized silica gel as a new sorbent for solid-phase extraction of heavy metal ions in water samples
- PMID: 35865198
- PMCID: PMC9260518
- DOI: 10.1039/d2ra02980d
Ionic liquid-immobilized silica gel as a new sorbent for solid-phase extraction of heavy metal ions in water samples
Abstract
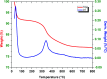
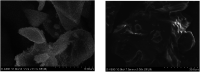
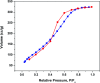
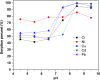
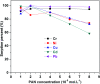
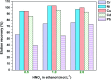
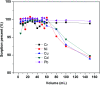
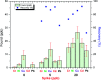
In the current study, we have developed a solid-phase extraction (SPE) method with novel C18-alkylimidazolium ionic liquid immobilized silica (SiO2-(CH2)3-Im-C18) for the preconcentration of trace heavy metals from aqueous samples as a prior step to their determination by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICPMS). The material was characterized by Fourier-transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA), Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS), and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) analysis. A mini-column packed with SiO2-(CH2)3-Im-C18 sorbent was used for the extraction of the metal ions complexed with 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphthol (PAN) from the water sample. The effects of pH, PAN concentration, length of the alkyl chain of the ionic liquid, eluent concentration, eluent volume, and breakthrough volume have been investigated. The SiO2-(CH2)3-Im-C18 allows the isolation and preconcentration of the heavy metal ions with enrichment factors of 150, 60, 80, 80, and 150 for Cr3+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+, respectively. The limits of detection (LODs) for Cr3+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ were 0.724, 11.329, 4.571, 0.112, and 0.819 μg L-1, respectively with the relative standard deviation (RSD) in the range of 0.941-1.351%.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Graphene oxide-silica composite coating hollow fiber solid phase microextraction online coupled with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for the determination of trace heavy metals in environmental water samples.Talanta. 2014 Jun;123:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2014.01.061. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Talanta. 2014. PMID: 24725857
-
Developing a highly selective method for preconcentration and determination of cobalt in water and nut samples using 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphthol and UV-visible spectroscopy.J Sci Food Agric. 2020 Mar 30;100(5):2272-2279. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10257. Epub 2020 Feb 6. J Sci Food Agric. 2020. PMID: 31930504
-
Magnetic materials as sorbents for metal/metalloid preconcentration and/or separation. A review.Anal Chim Acta. 2013 Jul 30;789:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.04.021. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Anal Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23856225 Review.
-
Synthesis of green nano sorbents for simultaneous preconcentration and recovery of heavy metals from water.Chemosphere. 2022 Jun;296:133971. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133971. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 35182527
-
Light-induced pH change and its application to solid phase extraction of trace heavy metals by high-magnetization Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2 nanoparticles followed by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry detection.Talanta. 2012 May 30;94:278-83. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2012.03.040. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Talanta. 2012. PMID: 22608448
References
-
- Li Y.-K. Yang T. Chen M.-L. Wang J.-H. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021;51:353–372. - PubMed
-
- Bolisetty S. Peydayesh M. Mezzenga R. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019;48:463–487. - PubMed
-
- Lu F. Astruc D. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018;356:147–164.
-
- Mohod C. Dhote J. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. 2013;2:2992–2996.
-
- Sall M. L. Diaw A. K. D. Gningue-Sall D. Efremova Aaron S. Aaron J.-J. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020;27:29927–29942. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

