Pneumococcal nasopharyngeal carriage in children under 5 years of age at an outpatient healthcare facility in Novi Sad, Serbia during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 35865274
- PMCID: PMC9294645
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijregi.2022.07.001
Pneumococcal nasopharyngeal carriage in children under 5 years of age at an outpatient healthcare facility in Novi Sad, Serbia during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
Objectives: To assess whether pneumococcal nasopharyngeal carriage among children aged 24-60 months reduced during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic in Novi Sad, Serbia, and to investigate the overall prevalence of carriage, serotype distribution and dominant serotypes 2-3 years after the introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine 10.
Design and methods: This prospective, observational study was conducted in February-March 2020, September-November 2020 and April-June 2021, enabling the comparison of results in the pre-pandemic/early pandemic period with two periods during the COVID-19 pandemic. Pneumococci were identified by standard microbiological methods. Serotype identification was performed using conventional multiplex polymerase chain reaction assays.
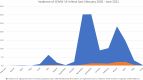
Results: Among 1623 children tested, 515 (31.7%, 95% confidence interval 29.4-34.0%) carried pneumococci. A significant increase in prevalence was found between February-March 2020 and September-November 2020 (P=0.0085), with no difference found between September-November 2020 and April-June 2021 (P=0.0524). Pneumococcal colonization was significantly higher in children who were fully vaccinated and among children who attended day care centres. The dominant serotypes were 15B, 6B, 19F, 11A, 6C, 6A, 3, 23F and 19A, representing 66.4% of all isolates.
Conclusions: This study found that pneumococcal nasopharyngeal carriage in children aged 24-60 months was high before the COVID-19 pandemic, and then increased during the pandemic. This rules out a major role of COVID-19 in the suppression of carriage and, probably, transmission.
Keywords: COVID-19; Nasopharyngeal colonization; Pneumococcal serotypes; Streptococcus pneumoniae.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
VP acts as the principal investigator for investigator-initiated sponsored studies related to the topic conducted on behalf of the Faculty of Medicine, University of Novi Sad, for which the Faculty obtained research grants from Pfizer and MSD. Outside the topic of work and in the last 36 months, VP, as an employee of the Faculty of Medicine, University of Novi Sads, obtained educational grants from Pfizer, GSK, MSD and Amicus; received paid fees for lectures from MSD, Pfizer and Sanofi Pasteur; served as a member of advisory boards for MSD, Sanofi Pasteur and Medison Pharma; and was a consultant at Expert Input Forums for MSD. MM has received paid fees for lectures from Pfizer, MSD, Sanofi Pasteur, GSK and Amicus for presentations at symposia. Outside the topic of work and in the last 36 months, MM served as a member of advisory boards for Pfizer, Sanofi Pasteur, GSK and Medison Pharma; and was a consultant at Expert Input Forums for MSD. Outside the topic of work and in the last 36 months, MR received paid fees for lectures from Sanofi Pasteur; and was a member of advisory boards for Sanofi Pasteur and Medison Pharma. The other authors do not report any conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Amin-Chowdhury Z, Aiano F, Mensah A, Sheppard CL, Litt D, Fry NK, et al. Impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on invasive pneumococcal disease and risk of pneumococcal coinfection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): prospective national cohort study, England. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;72:e65–e75. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andrejko K, Ratnasiri B, Hausdorff WP, Laxminarayan R, Lewnard JA. Antimicrobial resistance in paediatric Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates amid global implementation of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet Microb. 2021;2:e450–e460. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

