Neurological and Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of Antiphospholipid-Antibody Syndrome (APS)
- PMID: 35865415
- PMCID: PMC9293251
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.26022
Neurological and Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of Antiphospholipid-Antibody Syndrome (APS)
Abstract
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disorder mediated by the presence of a group of autoantibodies, specifically the anticardiolipin antibody (aCL), the beta-2 glycoprotein I (β2GPI), and the lupus anticoagulant (LA). Patients diagnosed with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) present with many symptoms, the most common being the consequence of thrombotic events that can be catastrophic and lead to mild to severe residual disabilities over a significant amount of time and can impair the quality of life. These events are often present in the younger population. Many times, these thrombotic events are heralded by a spectrum of psychiatric symptoms, which when worked up in the right direction may hint toward an oncoming thrombotic event and may potentially prevent those events by prompting primary prophylaxis treatment by the treating physician. In this review, we aim to comprehensively put forth the many neurological and neuropsychiatric manifestations of APS, their pathology, and management.
Keywords: antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (aps); autoimmune disorder; neuropsychiatric manifestations of aps; psychosis; stroke in young.
Copyright © 2022, Asif et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
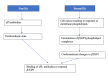
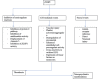
References
-
- International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:295–306. - PubMed
-
- Durcan L. Handbook of Systemic Autoimmune Diseases, Antiphospholipid Syndrome in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases, Volume 12. Vol. 17. New York: Elsevier; 2016. Epidemiology of the antiphospholipid syndrome; p. 30.
-
- Antiphospholipid syndrome. Schreiber K, Sciascia S, de Groot PG, et al. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18005. - PubMed
-
- International consensus statement on preliminary classification criteria for the antiphospholipid syndrome: report of an international workshop. Wilson WA, Gharavi AE, Koike T, et al. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Michael-Lockshin/publication/128965.... Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:1309–1311. - PubMed
-
- Antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical and immunologic manifestations and patterns of disease expression in a cohort of 1,000 patients. Cervera R, Piette JC, Font J, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:1019–1027. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
