Endothelial Cells as a Key Cell Type for Innate Immunity: A Focused Review on RIG-I Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 35865527
- PMCID: PMC9294349
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.951614
Endothelial Cells as a Key Cell Type for Innate Immunity: A Focused Review on RIG-I Signaling Pathway
Abstract
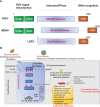
The vascular endothelium consists of a highly heterogeneous monolayer of endothelial cells (ECs) which are the primary target for bacterial and viral infections due to EC's constant and close contact with the bloodstream. Emerging evidence has shown that ECs are a key cell type for innate immunity. Like macrophages, ECs serve as sentinels when sensing invading pathogens or microbial infection caused by viruses and bacteria. It remains elusive how ECs senses danger signals, transduce the signal and fulfil immune functions. Retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I, gene name also known as DDX58) is an important member of RIG-I-like receptor (RLR) family that functions as an important pathogen recognition receptor (PRR) to execute immune surveillance and confer host antiviral response. Recent studies have demonstrated that virus infection, dsRNA, dsDNA, interferons, LPS, and 25-hydroxycholesterol (25-HC) can increase RIG-1 expression in ECs and propagate anti-viral response. Of translational significance, RIG-I activation can be inhibited by Panax notoginseng saponins, endogenous PPARγ ligand 15-PGJ2, tryptanthrin and 2-animopurine. Considering the pivotal role of inflammation and innate immunity in regulating endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis, here we provided a concise review of the role of RIG-I in endothelial cell function and highlight future direction to elucidate the potential role of RIG-I in regulating cardiovascular diseases as well as virus infectious disease, including COVID-19. Furthered understanding of RIG-I-mediated signaling pathways is important to control disorders associated with altered immunity and inflammation in ECs.
Keywords: DDX58; RIG-I; endothelial cells; immunity; inflammation.
Copyright © 2022 Xu, Jin and Weng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of the RIG-I pathway during influenza vaccination enhances the germinal center reaction, promotes T follicular helper cell induction, and provides a dose-sparing effect and protective immunity.J Virol. 2014 Dec;88(24):13990-4001. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02273-14. Epub 2014 Sep 24. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25253340 Free PMC article.
-
Human Hemoglobin Subunit Beta Functions as a Pleiotropic Regulator of RIG-I/MDA5-Mediated Antiviral Innate Immune Responses.J Virol. 2019 Jul 30;93(16):e00718-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00718-19. Print 2019 Aug 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31167908 Free PMC article.
-
Negative regulators of the RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway.Eur J Immunol. 2017 Apr;47(4):615-628. doi: 10.1002/eji.201646484. Eur J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28295214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and pathways of innate immune activation and regulation in health and cancer.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(11):3270-85. doi: 10.4161/21645515.2014.979640. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25625930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subcellular Localizations of RIG-I, TRIM25, and MAVS Complexes.J Virol. 2017 Jan 3;91(2):e01155-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01155-16. Print 2017 Jan 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 27807226 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Regulation of IFNβ expression: focusing on the role of its promoter and transcription regulators.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 15;14:1158777. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1158777. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37396372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rickettsia rickettsii virulence determinants RARP2 and RapL mitigate IFN-β signaling in primary human dermal microvascular endothelial cells.mBio. 2024 Apr 10;15(4):e0345023. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03450-23. Epub 2024 Mar 6. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38445878 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Immune Nanoparticles for Rapid and Non-Specific Activation of Antiviral and Antibacterial Immune Responses in Cattle, Swine, and Poultry.Animals (Basel). 2023 May 18;13(10):1686. doi: 10.3390/ani13101686. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37238119 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome sequencing promotes insights on the molecular mechanism of SKP-SC-EVs mitigating denervation-induced muscle atrophy.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Dec 12;51(1):9. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08952-x. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 38085347
-
The immune system in cardiovascular diseases: from basic mechanisms to therapeutic implications.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 May 23;10(1):166. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02220-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40404619 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li X, Fang P, Yang WY, Wang H, Yang X. IL-35, as a Newly Proposed Homeostasis-Associated Molecular Pattern, Plays Three Major Functions Including Anti-Inflammatory Initiator, Effector, and Blocker in Cardiovascular Diseases. Cytokine (2019) 122:154076. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.06.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

