Use of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Antagonists Is Associated With Attenuated IgG Antibody Response Against SARS-CoV-2 in Vaccinated Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- PMID: 35865529
- PMCID: PMC9294156
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.920333
Use of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Antagonists Is Associated With Attenuated IgG Antibody Response Against SARS-CoV-2 in Vaccinated Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
Introduction: Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) frequently receive immunomodulating treatment, which may render them at increased risk of an attenuated immune response upon vaccination. In this study, we assessed the effects of different types of commonly prescribed immunosuppressive medications on the serological response after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with IBD.
Methods: In this prospective observational cohort study, IgG antibody titers against SARS-CoV-2 were measured 2-10 weeks after completion of standard vaccination regimens in patients with IBD. Clinical characteristics, previous history of SARS-CoV-2 infection, type of vaccine (mRNA- or vector-based) and medication use were recorded at the time of sampling. Subsequently, a chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay was used for the quantitative determination of IgG antibodies against the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the S1 subunit of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2.
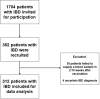
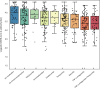
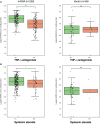
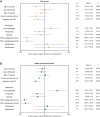
Results: Three hundred and twelve (312) patients with IBD were included (172 Crohn's disease [CD] and 140 ulcerative colitis [UC]). Seroconversion (defined as titer of >50 AU/ml) was achieved in 98.3% of patients. Antibody concentrations were significantly lower in patients treated with TNF-α-antagonists vs. non-users of TNF-α-antagonists (geometric mean [95% confidence interval]: 2204 [1655-2935] vs. 5002 [4089-6116] AU/ml, P<0.001). In multivariable models, use of TNF-α-antagonists (P<0.001), vector vaccines (P<0.001), age (>50 years) (P<0.01) and CD (P<0.05) were independently associated with lower anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers. In patients who received mRNA vaccines, users of thiopurines (either prescribed as monotherapy or in combination with biologicals) demonstrated significantly lower antibody titers compared to thiopurine non-users (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Despite reassuring findings that most patients with IBD have detectable antibodies after anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, TNF-α-antagonists were found to be strongly associated with an attenuated IgG antibody response after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, independent of vaccine type, the time elapsed after vaccination and blood sampling, prior SARS-CoV-2 infection and patient age. Patients treated with thiopurines and receiving mRNA-based vaccines demonstrated lower anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers compared with non-users.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; TNF-α-antagonists; antibody; inflammatory bowel disease; vaccination.
Copyright © 2022 Otten, Bourgonje, Horinga, van der Meulen, Festen, van Dullemen, Weersma, van Leer-Buter, Dijkstra and Visschedijk.
Conflict of interest statement
GD received research grants from Royal DSM and speaker’s fees from Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Takeda, Pfizer and Abbvie. RW acted as consultant for Takeda, received unrestricted research grants from Takeda, Johnson & Johnson, Tramedico and Ferring, and received speaker fees from MSD, Abbvie and Janssen Pharmaceuticals. MV has served on the advisory board for Janssen-Cilag and received a speaker’s fee from Takeda, outside the submitted work. The funders had no role in the design of the study, collection, analysis, or interpretation of data or in writing the manuscript. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

