Single-cell RNA Sequencing Analysis Reveals New Immune Disorder Complexities in Hypersplenism
- PMID: 35865544
- PMCID: PMC9294158
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.921900
Single-cell RNA Sequencing Analysis Reveals New Immune Disorder Complexities in Hypersplenism
Abstract
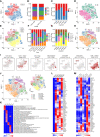
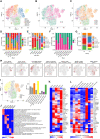
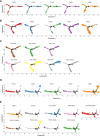
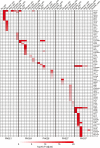
Hypersplenism (HS) is a concomitant symptom of liver or blood disease. Not only does the treatment of HS face challenges, but the transcriptome of individual cells is also unknown. Here, the transcriptional profiles of 43,037 cells from four HS tissues and one control tissue were generated by the single-cell RNA sequencing and nine major cell types, including T-cells, B-cells, NK cells, hematopoietic stem cells, neutrophil cells, mast cells, endothelial cells, erythrocytes, and dendritic cells were identified. Strikingly, the main features were the lack of CCL5+ B-cells in HS and the presence of SESN1+ B cells in HS with hepatocellular carcinoma (HS-HCC). In cell-cell interaction analysis, CD74-COPA and CD94-HLA-E in HS were found to be up-regulated. We further explored HS-specifically enriched genes (such as FKBP5, ADAR, and RPS4Y1) and found that FKBP5 was highly expressed in HCC-HS, leading to immunosuppression. Taken together, this research provides new insights into the genetic characteristics of HS via comprehensive single-cell transcriptome analysis.
Keywords: B-cells; T-cells; hypersplenism; immune disorder; single-cell RNA sequencing.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Chen, Song, Wang, Zhang, Zhao and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

