Improvement of Cs detection performance and formation of CsCl and Cs nanoparticles by tuning graphene oxide quantum dot-based nanocomposite
- PMID: 35865579
- PMCID: PMC9257967
- DOI: 10.1039/d2ra02091b
Improvement of Cs detection performance and formation of CsCl and Cs nanoparticles by tuning graphene oxide quantum dot-based nanocomposite
Abstract
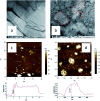
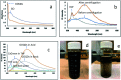
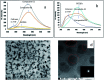
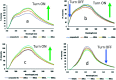
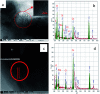
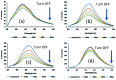
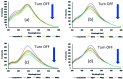
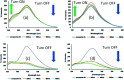
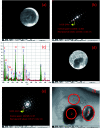
A new nanocomposite was developed using functionalized graphene oxide quantum dots (GOQDs) with cesium green molecules for the first time. Although the cesium green molecule works effectively only in the solid-state, without water, and in basic conditions, the functionalized GOQDs with cesium green made the nanocomposite work well as a cesium (Cs) detector in mixed solution (distilled water/THF). The nanocomposite can be employed as a Cs detector in both acidic and basic conditions. The present study revealed that the nanocomposite of GOQDs with cesium green showed an enhanced photoluminescence in basic conditions, while the intensity of the photoluminescence in acidic conditions is the superposition of the photoluminescence of the corresponding components. The photoluminescence of the nanocomposite was quenched (turned OFF) after Cs treatment in basic conditions. On the other hand, in the acidic conditions it was found that the photoluminescence intensity of this nanocomposite was enhanced (turned ON) by the Cs addition in two different Cs concentrations, 0.06 mmol L-1 and 0.12 mmol L-1. In addition, the movement of the nanocomposite (after Cs addition) under the electron beams through TEM measurement was observed. The formation of CsCl and Cs nanoparticles was identified. Specifically, the Cs cluster occurrence is discussed by taking into account the mobility effect of the adatoms on the composite layer under electron beam irradiation.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Basuki T. Miyashita S. Tsujimoto M. Nakashima S. “Deposition density of 134Cs and 137Cs and particle size distribution of soil and sediment profile in Hibara Lake area, Fukushima: an investigation of 134Cs and 137Cs indirect deposition into lake from surrounding area”. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018;316(3):1039–1046. doi: 10.1007/s10967-018-5809-1. - DOI
-
- TSUJIMOTO M. MIYASHITA S. NGUYEN H. T. NAKASHIMA S. “Monthly Change in Radioactivity Concentration of 137Cs, 134Cs, and 40K of Paddy Soil and Rice Plants in Fukushima Prefecture”. Radiat. Saf. Manag. 2020;19:10–22. doi: 10.12950/rsm.181219. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

