Epigenetic Mechanism of Early Life Stress-Induced Depression: Focus on the Neurotransmitter Systems
- PMID: 35865627
- PMCID: PMC9294154
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.929732
Epigenetic Mechanism of Early Life Stress-Induced Depression: Focus on the Neurotransmitter Systems
Abstract
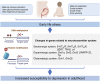
Depression has an alarmingly high prevalence worldwide. A growing body of evidence indicates that environmental factors significantly affect the neural development and function of the central nervous system and then induce psychiatric disorders. Early life stress (ELS) affects brain development and has been identified as a major cause of depression. It could promote susceptibility to stress in adulthood. Recent studies have found that ELS induces epigenetic changes that subsequently affect transcriptional rates of differentially expressed genes. The epigenetic modifications involved in ELS include histone modifications, DNA methylation, and non-coding RNA. Understanding of these genetic modifications may identify mechanisms that may lead to new interventions for the treatment of depression. Many reports indicate that different types of ELS induce epigenetic modifications of genes involved in the neurotransmitter systems, such as the dopaminergic system, the serotonergic system, the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-ergic system, and the glutamatergic system, which further regulate gene expression and ultimately induce depression-like behaviors. In this article, we review the effects of epigenetic modifications on the neurotransmitter systems in depression-like outcomes produced by different types of ELS in recent years, aiming to provide new therapeutic targets for patients who suffer from depression.
Keywords: depression; early life stress; epigenetics; methylation; neurotransmitter systems.
Copyright © 2022 Cheng, Su, Zhang, Jiang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

