Emerging Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Senescence
- PMID: 35865636
- PMCID: PMC9294638
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.869011
Emerging Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Senescence
Abstract
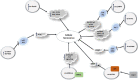
Senescence is defined as a gradual weakening of functional features of a living organism. Cellular senescence is a process that is principally aimed to remove undesirable cells by prompting tissue remodeling. This process is also regarded as a defense mechanism induced by cellular damage. In the course of oncogenesis, senescence can limit tumor progression. However, senescence participates in the pathoetiology of several disorders such as fibrotic disorders, vascular disorders, diabetes, renal disorders and sarcopenia. Recent studies have revealed contribution of different classes of non-coding RNAs in the cellular senescence. Long non-coding RNAs, microRNAs and circular RNAs are three classes of these transcripts whose contributions in this process have been more investigated. In the current review, we summarize the available literature on the impact of these transcripts in the cellular senescence.
Keywords: biomarker; epigenetics; expression; lncRNA; miRNA; senescence.
Copyright © 2022 Ghafouri-Fard, Khoshbakht, Hussen, Baniahmad, Branicki, Taheri and Eghbali.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
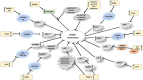
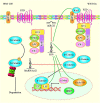
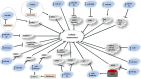
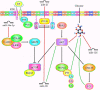
References
-
- Asadi M. H., Yaghoobi M. M. (2018). Long Noncoding RNA VIM-AS1 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression and Metastasis by Inducing EMT. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 97 (4), 279–288. - PubMed
-
- Auler M., Bergmeier V., Georgieva V. S., Pitzler L., Frie C., Nüchel J., et al. (2021). miR-127-3p Is an Epigenetic Activator of Myofibroblast Senescence Situated within the MicroRNA-Enriched Dlk1-Dio3‒Imprinted Domain on Mouse Chromosome 12. J. Investigative Dermatology 141 (4), 1076–1086. e3. 10.1016/j.jid.2020.11.011 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

