Exploring the Anti-inflammatory Effects of Protopine Total Alkaloids of Macleaya Cordata (Willd.) R. Br
- PMID: 35865876
- PMCID: PMC9294607
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.935201
Exploring the Anti-inflammatory Effects of Protopine Total Alkaloids of Macleaya Cordata (Willd.) R. Br
Abstract
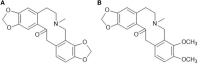
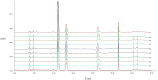
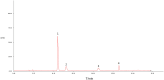
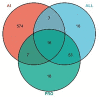
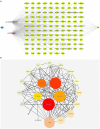
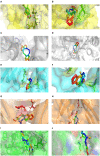
Macleaya cordata (Willd). R. Br. is a Chinese medicinal plant commonly used externally to treat inflammatory-related diseases such as arthritis, sores, and carbuncles. This study aimed to evaluate the anti-inflammatory activity of protopine total alkaloids (MPTAs) in Macleaya cordata (Willd.) R. Br. in vivo tests in rats with acute inflammation showed that MPTA (2.54 and 5.08 mg/kg) showed significant anti-inflammatory activity 6 h after carrageenan injection. Similarly, MPTA (3.67 and 7.33 mg/kg) showed significant anti-inflammatory activity in the mouse ear swelling test. In addition, the potential mechanisms of the anti-inflammatory effects of MPTA were explored based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. The two main active components of MPTA, protopine and allocryptopine, were identified, and the potential targets and signaling pathways of MPTA's anti-inflammatory effects were initially revealed using tools and databases (such as SwissTargetPrediction, GeneCards, and STRING) combined with molecular docking results. This study provides the basis for the application of MPTA as an anti-inflammatory agent.
Keywords: Macleaya cordata (Willd.) R. Br.; acute inflammation; anti-inflammatory; molecular docking; network pharmacology; protopine total alkaloids.
Copyright © 2022 Dong, Wang, Tang, Li, Jiang, Yang and Zeng.
Conflict of interest statement
Z-sT and C-hL were employed by the Hunan MICOLTA Biological Resources Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chen T, Shang Z. Commentary on Supplement to Medica. Hefei: Anhui Science and Technology Press; (2002).
-
- Ali I, Li J, Cui L, Zhao H, He Q, Wang D. Efficient extraction and purification of benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids from Macleaya cordata (Willd) R. Br by combination of ultrahigh pressure extraction and pH-zone-refining counter-current chromatography with anti-breast cancer activity in vitro. Phytochem Anal. (2021) 32:423–32. 10.1002/pca.2990 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

