HIF-1α in Osteoarthritis: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Implications
- PMID: 35865944
- PMCID: PMC9294386
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.927126
HIF-1α in Osteoarthritis: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
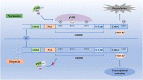
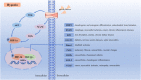
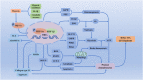
Osteoarthritis is a common age-related joint degenerative disease. Pain, swelling, brief morning stiffness, and functional limitations are its main characteristics. There are still no well-established strategies to cure osteoarthritis. Therefore, better clarification of mechanisms associated with the onset and progression of osteoarthritis is critical to provide a theoretical basis for the establishment of novel preventive and therapeutic strategies. Chondrocytes exist in a hypoxic environment, and HIF-1α plays a vital role in regulating hypoxic response. HIF-1α responds to cellular oxygenation decreases in tissue regulating survival and growth arrest of chondrocytes. The activation of HIF-1α could regulate autophagy and apoptosis of chondrocytes, decrease inflammatory cytokine synthesis, and regulate the chondrocyte extracellular matrix environment. Moreover, it could maintain the chondrogenic phenotype that regulates glycolysis and the mitochondrial function of osteoarthritis, resulting in a denser collagen matrix that delays cartilage degradation. Thus, HIF-1α is likely to be a crucial therapeutic target for osteoarthritis via regulating chondrocyte inflammation and metabolism. In this review, we summarize the mechanism of hypoxia in the pathogenic mechanisms of osteoarthritis, and focus on a series of therapeutic treatments targeting HIF-1α for osteoarthritis. Further clarification of the regulatory mechanisms of HIF-1α in osteoarthritis may provide more useful clues to developing novel osteoarthritis treatment strategies.
Keywords: HIF-1α; chondrocytes; glycolysis; hypoxia; mitophagy; osteoarthritis.
Copyright © 2022 Zeng, Wang and Hua.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of HIF-1α in hypoxic metabolic reprogramming in osteoarthritis.Pharmacol Res. 2025 Mar;213:107649. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2025.107649. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Pharmacol Res. 2025. PMID: 39947451 Review.
-
Role of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in osteoarthritis.Joint Bone Spine. 2015 May;82(3):144-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2014.10.003. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Joint Bone Spine. 2015. PMID: 25553838 Review.
-
miRNA-411 Regulates Chondrocyte Autophagy in Osteoarthritis by Targeting Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α).Med Sci Monit. 2020 Feb 19;26:e921155. doi: 10.12659/MSM.921155. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32072994 Free PMC article.
-
HIF-1alpha controls extracellular matrix synthesis by epiphyseal chondrocytes.J Cell Sci. 2003 May 1;116(Pt 9):1819-26. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00385. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12665562
-
Flavonoid Compound Icariin Activates Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α in Chondrocytes and Promotes Articular Cartilage Repair.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 3;11(2):e0148372. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148372. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26841115 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of the oral administration of glycosaminoglycans with or without native type II collagen on the articular cartilage transcriptome in an osteoarthritic-induced rabbit model.Genes Nutr. 2024 Sep 4;19(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12263-024-00749-2. Genes Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39232650 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of aging-related biomarkers and immune infiltration characteristics in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics analysis and machine learning.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 12;14:1168780. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1168780. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37503333 Free PMC article.
-
Plant molecules reinforce bone repair: Novel insights into phenol-modified bone tissue engineering scaffolds for the treatment of bone defects.Mater Today Bio. 2023 Dec 21;24:100920. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100920. eCollection 2024 Feb. Mater Today Bio. 2023. PMID: 38226013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and analysis of RNA-5-methylcytosine-related key genes in osteoarthritis.BMC Genomics. 2023 Sep 12;24(1):539. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09651-4. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37700248 Free PMC article.
-
The role of targeting glucose metabolism in chondrocytes in the pathogenesis and therapeutic mechanisms of osteoarthritis: a narrative review.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Mar 6;15:1319827. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1319827. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38510704 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akaraphutiporn E., Bwalya E. C., Kim S., Sunaga T., Echigo R., Okumura M. (2020). Effects of Pentosan Polysulfate on Cell Proliferation, Cell Cycle Progression and Cyclin-dependent Kinases Expression in Canine Articular Chondrocytes. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 82 (8), 1209–1218. 10.1292/jvms.20-0091 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balogh E., Tóth A., Méhes G., Trencsényi G., Paragh G., Jeney V. (2019). Hypoxia Triggers Osteochondrogenic Differentiation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in an HIF-1 (Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1)-Dependent and Reactive Oxygen Species-dependent Manner. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 39 (6), 1088–1099. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312509 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

